Urine N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and plasma proenkephalin are promising biomarkers for early diagnosis of cardiorenal syndrome type 1 in acute decompensated heart failure: a prospective, double-center, observational study in real-world
- PMID: 36000917
- PMCID: PMC9423828
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2114367
Urine N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and plasma proenkephalin are promising biomarkers for early diagnosis of cardiorenal syndrome type 1 in acute decompensated heart failure: a prospective, double-center, observational study in real-world
Abstract
Background: Patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) show cardiorenal syndrome type 1 (CRS-1) are more likely to have a poor outcome. However, the current criteria often lead to delayed CRS-1 diagnosis. Therefore, we evaluated the predictive value of plasma proenkephalin (pPENK) and urine NT-proBNP (uNT-proBNP) for early diagnosis of CRS-1 and vulnerable-phase prognosis in ADHF patients.
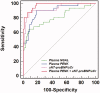
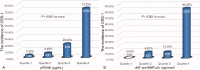
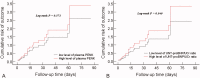
Methods: The plasma NT-proBNP (pNT-proBNP), pPENK, and uNT-proBNP were measured in 121 ADHF patients on admission. The plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (pNGAL) was chosen as the reference. Logistic regression was used to determine the predictors of CRS-1. The area under the receiver operating curves (ROCs) was calculated to assess the early diagnostic value of pNGAL, pPENK, and uNT-proBNP/uCr for CRS-1. To evaluate the prognostic risk of factors for the 90-d outcomes of all ADHF patients, the Cox regression was performed and the cumulative risk curve was plotted.
Results: We found that pPENK [OR 1.093 (95% CI 1.022-1.169), p = 0.010; AUROC = 0.899 (95% CI 0.831-0.946)] and uNT-proBNP/uCr ratio [OR 1.015 (95% CI 1.003-1.028), p = 0.012; AUROC = 0.934 (95% CI 0.874-0.971)] could independently predict the occurrence of CRS-1 in hospitalized patients with ADHF. The pPENK [HR 1.014 (95% CI 1.000-1.042), p = 0.044] and uNT-proBNP/uCr ration [HR 0.998 (95% CI 0.997-1.000), p = 0.045] were also independent predictors of the risk of HF readmission or all-cause death 90 d after discharge in ADHF patients.
Conclusions: The newly found pPENK and noninvasive test of uNT-proBNP/uCr ratio (pg/nmol) on admission may be two promising novel predictive biomarkers for early diagnosis of CRS-1 occurrence and vulnerable-phase outcomes in ADHF patients.
Keywords: Cardiorenal syndrome type 1; acute decompensated heart failure; prediction; proenkephalin; urine N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors of this manuscript to confirm that no author has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Competing Risk of Cardiac Status and Renal Function During Hospitalization for Acute Decompensated Heart Failure.JACC Heart Fail. 2015 Oct;3(10):751-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2015.05.009. JACC Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 26449995
-
Myocardial fibrosis combined with NT-proBNP improves the accuracy of survival prediction in ADHF patients.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 May 28;21(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02083-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34049488 Free PMC article.
-
Change in the NT-proBNP/Mature BNP Molar Ratio Precedes Worsening Renal Function in Patients With Acute Heart Failure: A Novel Predictor Candidate for Cardiorenal Syndrome.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 3;8(17):e011468. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011468. Epub 2019 Aug 23. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31441355 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of plasma biomarkers in discharged heart failure patients: role of plasma NT-proBNP.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016 Apr;64(2):157-64. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016. PMID: 26373781 Review.
-
N-Terminal B-type Natriuretic Peptide in Heart Failure.Heart Fail Clin. 2018 Jan;14(1):27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2017.08.004. Heart Fail Clin. 2018. PMID: 29153198 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insight in Cardiorenal Syndrome: From Biomarkers to Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 7;24(6):5089. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065089. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proenkephalin as a Novel Prognostic Marker in Heart Failure Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 3;24(5):4887. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054887. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902318 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value and utility of commonly used biomarkers of cardiac and renal function in cardiorenal syndromes: a narrative review.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2023 Oct 15;33(3):030502. doi: 10.11613/BM.2023.030502. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2023. PMID: 37545695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proenkephalin 119-159 in Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 13;14(8):2657. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082657. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proenkephalin as a biomarker correlates with acute kidney injury: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Crit Care. 2023 Dec 7;27(1):481. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04747-5. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 38057904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ronco C, Cicoira M, McCullough PA.. Cardiorenal syndrome type 1: pathophysiological crosstalk leading to combined heart and kidney dysfunction in the setting of acutely decompensated heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(12):1031–1042. - PubMed
-
- Bader FM, Attallah N.. Insights into cardiorenal interactions in acute decompensated heart failure. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2017;32(2):203–208. - PubMed
-
- Greene SJ, Fonarow GC, Vaduganathan M, et al. . The vulnerable phase after hospitalization for heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015;12(4):220–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
