Synergistic effect of low-frequency ultrasound and antibiotics on the treatment of Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in mice
- PMID: 36001465
- PMCID: PMC9618311
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.14134
Synergistic effect of low-frequency ultrasound and antibiotics on the treatment of Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in mice
Abstract
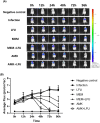
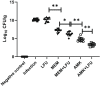
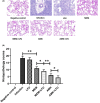
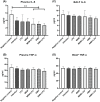
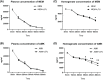
The antibiotic-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp) has become a significant crisis in treating pneumonia. Low-frequency ultrasound (LFU) is promising to overcome the obstacles. Mice were infected with bioluminescent Kp Xen39 by intratracheal injection to study the therapeutic effect of LFU in combination with antibiotics. The counts per second (CPS) were assessed with an animal biophoton imaging system. Bacterial clearance, histopathology, and the concentrations of cytokines were determined to evaluate the therapeutic effect. LC-MS/MS was used to detect the distribution of antibiotics in the lung and plasma. LFU in combination with meropenem (MEM) or amikacin (AMK) significantly improved the behavioural state of mice. The CPS of the LFU combination group were more significantly decreased compared with those of the antibiotic alone groups. The average colony-forming units of lung tissue in the LFU combination groups were also lower than those of the antibiotic groups. Although no significant changes of cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α) in plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were observed, LFU in combination with antibiotics showed less inflammatory damage from histopathological results compared with the antibiotic-alone groups. Moreover, 10 min of LFU treatment promoted the distribution of MEM and AMK in mouse lung tissue at 60 and 30 min, respectively, after dosage. LFU could enhance the effectiveness of MEM and AMK in the treatment of Kp-induced pneumonia, which might be attributed to the fact that LFU could promote the distribution of antibiotics in lung tissue and reduce inflammatory injury.
© 2022 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to be declared. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of low-frequency ultrasound combined with anti-MRSA agents on the mouse model of pulmonary infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Feb 7;12(3):e0101623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01016-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38323827 Free PMC article.
-
Low-frequency ultrasound alleviates pulmonary inflammation induced by Klebsiella pneumoniae in mice by inhibiting the TNFR1/NF-κB pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 May 8;154:114574. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114574. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40188523
-
Low-Frequency Ultrasound Enhances Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents against Klebsiella pneumoniae Biofilm.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jan 3;2020:5916260. doi: 10.1155/2020/5916260. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31998794 Free PMC article.
-
Inhaled amikacin for pneumonia treatment and dissemination prevention: an experimental model of severe monolateral Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia.Crit Care. 2023 Feb 14;27(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04331-x. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 36788582 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of meropenem and amikacin combination therapy against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae mouse model of pneumonia.J Infect Chemother. 2020 Dec;26(12):1237-1243. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.07.002. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Infect Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32868198
Cited by
-
Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound: A Physical Stimulus with Immunomodulatory and Anti-inflammatory Potential.Ann Biomed Eng. 2024 Aug;52(8):1955-1981. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03523-y. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 38683473 Review.
-
Effects of low-frequency ultrasound combined with anti-MRSA agents on the mouse model of pulmonary infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Feb 7;12(3):e0101623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01016-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38323827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azagury, A. , Khoury, L. , Enden, G. & Kost, J. (2014) Ultrasound mediated transdermal drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 72, 127–143. - PubMed
-
- Baker, K.G. , Robertson, V.J. & Duck, F.A. (2001) A review of therapeutic ultrasound: biophysical effects. Physical Therapy, 81, 1351–1358. - PubMed
-
- Bartoloni, A. , Strohmeyer, M. , Corti, G. , Buonomini, M.I. , Franchino, L. , Romanelli, G. et al. (1999) Multicenter randomized trial comparing meropenem (1.5 g daily) and imipenem/cilastatin (2 g daily) in the hospital treatment of community‐acquired pneumonia. Drugs under Experimental and Clinical Research, 25, 243–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

