Mechanistic insights into intramembrane proteolysis by E. coli site-2 protease homolog RseP
- PMID: 36001659
- PMCID: PMC9401612
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abp9011
Mechanistic insights into intramembrane proteolysis by E. coli site-2 protease homolog RseP
Abstract
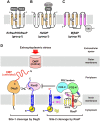
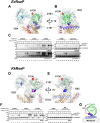
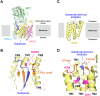
Site-2 proteases are a conserved family of intramembrane proteases that cleave transmembrane substrates to regulate signal transduction and maintain proteostasis. Here, we elucidated crystal structures of inhibitor-bound forms of bacterial site-2 proteases including Escherichia coli RseP. Structure-based chemical modification and cross-linking experiments indicated that the RseP domains surrounding the active center undergo conformational changes to expose the substrate-binding site, suggesting that RseP has a gating mechanism to regulate substrate entry. Furthermore, mutational analysis suggests that a conserved electrostatic linkage between the transmembrane and peripheral membrane-associated domains mediates the conformational changes. In vivo cleavage assays also support that the substrate transmembrane helix is unwound by strand addition to the intramembrane β sheet of RseP and is clamped by a conserved asparagine residue at the active center for efficient cleavage. This mechanism underlying the substrate binding, i.e., unwinding and clamping, appears common across distinct families of intramembrane proteases that cleave transmembrane segments.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Substrate recognition and binding by RseP, an Escherichia coli intramembrane protease.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 11;283(15):9562-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709984200. Epub 2008 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18268014
-
Involvement of a Membrane-Bound Amphiphilic Helix in Substrate Discrimination and Binding by an Escherichia coli S2P Peptidase RseP.Front Microbiol. 2020 Nov 27;11:607381. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.607381. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33329500 Free PMC article.
-
S2P intramembrane protease RseP degrades small membrane proteins and suppresses the cytotoxicity of intrinsic toxin HokB.mBio. 2023 Aug 31;14(4):e0108623. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01086-23. Epub 2023 Jul 6. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37409810 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural insights into intramembrane metalloprotease mechanisms.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1828(12):2873-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.03.032. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24099006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical Characterization of Function and Structure of RseP, an Escherichia coli S2P Protease.Methods Enzymol. 2017;584:1-33. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.09.044. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28065260 Review.
Cited by
-
Maintaining the Integral Membrane Proteome: Revisiting the Functional Repertoire of Integral Membrane Proteases.Chembiochem. 2025 May 5;26(9):e202500048. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202500048. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Chembiochem. 2025. PMID: 40056010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substrate engagement by the intramembrane metalloprotease SpoIVFB.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 17;15(1):8276. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52634-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39419996 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structure of the bacterial intramembrane metalloprotease RseP in the substrate-bound state.Sci Adv. 2025 Feb 28;11(9):eadu0925. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu0925. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40009668 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Drug Responses to Human β2AR Using Native Mass Spectrometry.ACS Omega. 2023 Jun 28;8(27):24544-24551. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02737. eCollection 2023 Jul 11. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37457453 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for regulation of a CBASS-CRISPR-Cas defense island by a transmembrane anti-σ factor and its ECF σ partner.Sci Adv. 2024 Oct 25;10(43):eadp1053. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp1053. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39454004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown M. S., Ye J., Rawson R. B., Goldstein J. L., Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: A control mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Cell 100, 391–398 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Beard H. A., Barniol-Xicota M., Yang J., Verhelst S. H. L., Discovery of cellular roles of intramembrane proteases. ACS Chem. Biol. 14, 2372–2388 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Kühnle N., Dederer V., Lemberg M. K., Intramembrane proteolysis at a glance: From signalling to protein degradation. J. Cell Sci. 132, jcs217745 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Suzuki N., Cheung T. T., Cai X. D., Odaka A., Otvos L. Jr., Eckman C., Golde T. E., Younkin S. G., An increased percentage of long amyloid β protein secreted by familial amyloid β protein precursor (βAPP717) mutants. Science 264, 1336–1340 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Selkoe D. J., Alzheimer’s disease: Genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 81, 741–766 (2001). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

