Untwisted α-Synuclein Filaments Formed in the Presence of Lipid Vesicles
- PMID: 36001818
- PMCID: PMC10289115
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00283
Untwisted α-Synuclein Filaments Formed in the Presence of Lipid Vesicles
Abstract
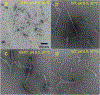
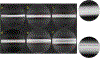
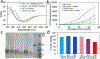
Accumulation of filamentous aggregates of α-synuclein is a pathological hallmark of several neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson's disease (PD). The interaction between α-synuclein and phospholipids has been shown to play a critical role in the aggregation of α-synuclein. Most structural studies have, however, been focused on α-synuclein filaments formed in the absence of lipids. Here, we report the structural investigation of α-synuclein filaments assembled under the quiescent condition in the presence of anionic lipid vesicles using electron microscopy (EM), including cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Our transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses reveal that α-synuclein forms curly protofilaments at an early stage of aggregation. The flexible protofilaments were then converted to long filaments after a longer incubation of 30 days. More detailed structural analyses using cryo-EM reveal that the long filaments adopt untwisted structures with different diameters, which have not been observed in previous α-synuclein fibrils formed in vitro. The untwisted filaments are rather similar to straight filaments with no observable twist that are extracted from patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Our structural studies highlight the conformational diversity of α-synuclein filaments, requiring additional structural investigation of not only more ex vivo α-synuclein filaments but also in vitro α-synuclein filaments formed in the presence of diverse cofactors to better understand the molecular basis of diverse molecular conformations of α-synuclein filaments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tau induces formation of α-synuclein filaments with distinct molecular conformations.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 May 21;554:145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.03.091. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33798940 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of α-synuclein filaments from human brains with Lewy pathology.Nature. 2022 Oct;610(7933):791-795. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05319-3. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36108674 Free PMC article.
-
The 3D structure of lipidic fibrils of α-synuclein.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 10;13(1):6810. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34552-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36357403 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Lipids Interacting with α-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2017;7(3):433-450. doi: 10.3233/JPD-171103. J Parkinsons Dis. 2017. PMID: 28671142 Review.
-
Neuropathology and molecular diagnosis of Synucleinopathies.Mol Neurodegener. 2021 Dec 18;16(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00501-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 34922583 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cryo-EM structures of pathogenic fibrils and their impact on neurodegenerative disease research.Neuron. 2024 Jul 17;112(14):2269-2288. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.05.012. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Neuron. 2024. PMID: 38834068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrastructures of α-Synuclein Filaments in Synucleinopathy Brains and Experimental Models.J Mov Disord. 2024 Jan;17(1):15-29. doi: 10.14802/jmd.23213. Epub 2023 Nov 22. J Mov Disord. 2024. PMID: 37990381 Free PMC article.
-
Increased unsaturated lipids underlie lipid peroxidation in synucleinopathy brain.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Nov 14;10(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01469-7. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 36376990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goedert M (2001) Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci 2, 492–501. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

