Polymerisation-Induced Self-Assembly of Graft Copolymers
- PMID: 36002384
- PMCID: PMC9828155
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202210518
Polymerisation-Induced Self-Assembly of Graft Copolymers
Abstract
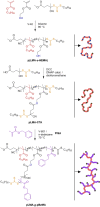
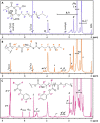
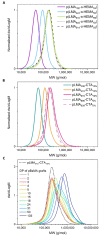
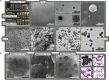
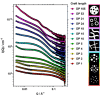
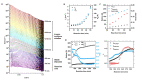
We report the polymerisation-induced self-assembly of poly(lauryl methacrylate)-graft-poly(benzyl methacrylate) copolymers during reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) grafting from polymerisation in a backbone-selective solvent. Electron microscopy images suggest the phase separation of grafts to result in a network of spherical particles, due to the ability of the branched architecture to freeze chain entanglements and to bridge core domains. Small-angle X-ray scattering data suggest the architecture promotes the formation of multicore micelles, the core morphology of which transitions from spheres to worms, vesicles, and inverted micelles with increasing volume fraction of the grafts. A time-resolved SAXS study is presented to illustrate the formation of the inverted phase during a polymerisation. The grafted architecture gives access to unusual morphologies and provides exciting new handles for controlling the polymer structure and material properties.
Keywords: Graft Copolymer; PISA; Polymerization; RAFT; Self-Assembly.
© 2022 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- J.-M. Boutillier, J.-P. Disson, M. Havel, R. Inoubli, S. Magnet, C. Laurichesse, D. Labouvier, Adhesives & Sealants Industry Magazine, 2013.
-
- Niitani T., Amaike M., Nakano H., Dokko K., Kanamura K., J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, A577.
-
- Goldfeld D. J., Silver E. S., Radlauer M. R., Hillmyer M. A., ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 817.
-
- Blanazs A., Verber R., Mykhaylyk O. O., Ryan A. J., Heath J. Z., Douglas C. W., Armes S. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9741. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

