The global survival rate of graft and patient in kidney transplantation of children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36002803
- PMCID: PMC9404642
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-022-03545-2
The global survival rate of graft and patient in kidney transplantation of children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: This study is a systematic review and meta-analysis on published studies about the Global Survival Rate of Graft and Patients in the Kidney Transplantation of children.
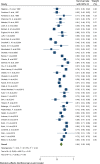
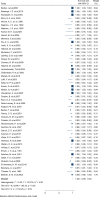
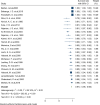
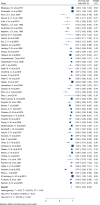
Methods: Studies that investigated the survival rate of kidney transplants published until the 30th of December 2020 were selected using a systematic search strategy in the following databases: Medline, Embase, Scopus, ProQuest, ISI Web of Science, and Cochrane. The extracted data were entered into the Excel software and STATA 16.0. The search identified 6007 study references. From the total, we excluded 1348 duplicates, 3688 reference titles and abstracts that were deemed irrelevant, and 846 references that were not original articles (i.e., letter, commentary, review) or did not meet the inclusion criteria. As such, 89 studies involving 12,330 participants were included in this meta-analysis.
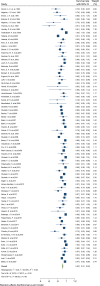
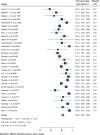
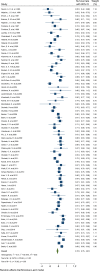
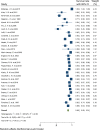
Results: In this study 1, 3, 5, 7 and 10-year survival rates of graft were estimated to be 92, 83, 74.40, 67.10, and 63.50%, respectively. Also, 1, 3, 5, 7 and 10-year survival rates of patients were estimated to be 99.60, 97.30, 95.20, 74.60, and 97.90%, respectively.
Conclusions: The findings suggest differences in graft and patient survival among children with kidney transplants. Although differences in ethnic origin, incompatibility with deceased donor kidneys, and types of kidney disease are unavoidable, interventions to improve preventive and living-donor transplantation are particularly needed in minority groups. In addition, more research is needed to establish and address the contribution of medical and sociocultural barriers to preferential treatment of these groups.
Keywords: Graft survival; Kidney transplantation; Meta-analysis; Patient survival.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
The OPTN/UNOS Renal Transplant Registry.Clin Transpl. 2005:1-16. Clin Transpl. 2005. PMID: 17424721
-
Graft and Patient Survival Rates in Kidney Transplantation, and Their Associated Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2021 Aug;50(8):1555-1563. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v50i8.6801. Iran J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34917526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The UNOS renal transplant registry.Clin Transpl. 2001:1-18. Clin Transpl. 2001. PMID: 12211771
-
Clinical outcomes after ABO-incompatible renal transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet. 2019 May 18;393(10185):2059-2072. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32091-9. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31006573
Cited by
-
Clinical profile and outcome of kidney transplantation at Muhimbili National Hospital, Tanzania.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Sep 28;25(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03765-x. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39342167 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Pediatric Kidney Transplant Rejection: Its Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Management Strategies.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(18):3571-3590. doi: 10.2174/0109298673333693240806160544. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39136521 Review.
-
Predicting Cellular Rejection of Renal Allograft Based on the Serum Proteomic Fingerprint.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 29;25(7):3844. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073844. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612654 Free PMC article.
-
Riding the wave: A grounded theory of transplant transition in adolescents and youth adults.Health Care Transit. 2023 Sep 15;1:100019. doi: 10.1016/j.hctj.2023.100019. eCollection 2023. Health Care Transit. 2023. PMID: 39713017 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective analysis of prenatal genetic results in fetal hydronephrosis.PLoS One. 2025 May 22;20(5):e0324734. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324734. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40403082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghojogh MG, Salarilak S, Afshari AT, Khalkhali HR, Mohammadi-Fallah MR, Makhdoomi K. Impact of type of donor on graft and patient survival rate in kidney transplanted patients in Iran. J Renal Inj Prev. 2018;7(4):264–268. doi: 10.15171/jrip.2018.59. - DOI
-
- Ghojogh MG, Salarilak S, Afshari AT, Khalkhali HR, Mohammadi-Fallah MR, Makhdoomi K. The effect of urinary tract infection on patient and graft survival rate in a group of kidney transplanted patients. J Renal Inj Prev. 2018;7(4):292–296. doi: 10.15171/jrip.2018.64. - DOI
-
- Zeba Z, Fatema K, Sumit AF, Zinnat R, Ali L. Early screening of chronic kidney disease patients among the asymptomatic adult population in Bangladesh J Prevent Epidemiol. 2020;5(1):e10-e.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

