The key amino acid sites 199-205, 269, 319, 321 and 324 of ALV-K env contribute to the weaker replication capacity of ALV-K than ALV-A
- PMID: 36002842
- PMCID: PMC9400301
- DOI: 10.1186/s12977-022-00598-0
The key amino acid sites 199-205, 269, 319, 321 and 324 of ALV-K env contribute to the weaker replication capacity of ALV-K than ALV-A
Abstract
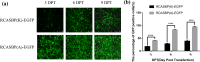
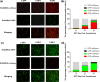
Background: Avian leukosis virus (ALV) is an infectious retrovirus, that mainly causes various forms of tumours, immunosuppression, a decreased egg production rate and slow weight gain in poultry. ALV consists of 11 subgroups, A-K, among which ALV-K is an emerging subgroup that has become prevalent in the past 10 years. Most ALV-K isolates showed weak replication ability and pathogenicity. In this study, the weak replication ability of ALV-K was explored from the perspective of the interaction between ALV-K gp85 and the Tva receptor.
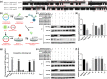
Methods: Fourteen soluble recombinant ALV-A/K gp85 chimeric proteins were constructed by substituting the sequence difference regions (hr1, hr2 and vr3) of the ALV-A gp85 protein with the skeleton ALV-K gp85 protein for co-IP and competitive blocking tests.
Results: The binding capacity of ALV-K gp85 to Tva was significantly weaker than that of ALV-A gp85 (P < 0.05) and the key amino acid sites 199-205, 269, 319, 321 and 324 of ALV-K env contributed to the weaker replication capacity of ALV-K than ALV-A.
Conclusions: This is the first study to reveal the molecular factors of the weak replication ability of ALV-K from the perspective of the interaction of ALV-K gp85 to Tva, providing a basis for further elucidation of the infection mechanism of ALV-K.
Keywords: Avian leukosis virus K subgroup; Binding capacity; Env; Recombinant chimaeras; Tva receptor.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
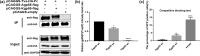
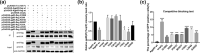
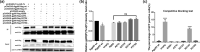
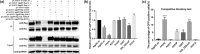
Similar articles
-
Gp37 Regulates the Pathogenesis of Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup J via Its C Terminus.J Virol. 2020 May 18;94(11):e02180-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02180-19. Print 2020 May 18. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32213616 Free PMC article.
-
The Bipartite Sequence Motif in the N and C Termini of gp85 of Subgroup J Avian Leukosis Virus Plays a Crucial Role in Receptor Binding and Viral Entry.J Virol. 2020 Oct 27;94(22):e01232-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01232-20. Print 2020 Oct 27. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32878894 Free PMC article.
-
Single Amino Acids G196 and R198 in hr1 of Subgroup K Avian Leukosis Virus Glycoprotein Are Critical for Tva Receptor Binding.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 16;11:596586. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.596586. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33391214 Free PMC article.
-
Recombination of variable and host range regions of glycoprotein gp85 in different avian leukosis virus subgroup K isolates.Arch Virol. 2024 Jun 29;169(7):155. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06083-7. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 38951272
-
Avian Leucosis Virus-Host Interaction: The Involvement of Host Factors in Viral Replication.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:907287. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.907287. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35693802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Avian Leukosis: Will We Be Able to Get Rid of It?Animals (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;13(14):2358. doi: 10.3390/ani13142358. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The phylogenetic analysis of the new emerging ALV-K revealing the co-prevailing of multiple clades in chickens and a proposal for the classification of ALV-K.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Jul 28;10:1228109. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1228109. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37576830 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

