Dietary protein levels changed the hardness of muscle by acting on muscle fiber growth and the metabolism of collagen in sub-adult grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)
- PMID: 36002862
- PMCID: PMC9404606
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-022-00747-7
Dietary protein levels changed the hardness of muscle by acting on muscle fiber growth and the metabolism of collagen in sub-adult grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)
Abstract
Background: Nutrient regulation has been proven to be an effective way to improve the flesh quality in fish. As a necessary nutrient for fish growth, protein accounts for the highest proportion in the fish diet and is expensive. Although our team found that the effect of protein on the muscle hardness of grass carp was probably related to an increased collagen content, the mechanism for this effect has not been deeply explored. Moreover, few studies have explored the protein requirements of sub-adult grass crap (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Therefore, the effects of different dietary protein levels on the growth performance, nutritional value, muscle hardness, muscle fiber growth, collagen metabolism and related molecule expression in grass carp were investigated.
Methods: A total of 450 healthy grass carp (721.16 ± 1.98 g) were selected and assigned randomly to six experimental groups with three replicates each (n = 25/replicate), and were fed six diets with 15.91%, 19.39%, 22.10%, 25.59%, 28.53% and 31.42% protein for 60 d.
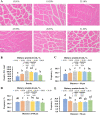
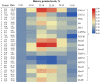
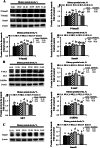
Results: Appropriate levels of dietary protein increased the feed intake, percentage weight gain, specific growth rate, body composition, unsaturated fatty acid content in muscle, partial free amino acid content in muscle, and muscle hardness of grass carp. These protein levels also increased the muscle fiber density, the frequency of new muscle fibers, the contents of collagen and IGF-1, and the enzyme activities of prolyl 4-hydroxylases and lysyloxidase, and decreased the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2. At the molecular level, the optimal dietary protein increased collagen type I α1 (Colα1), Colα2, PI3K, Akt, S6K1, La ribonucleoprotein domain family member 6a (LARP6a), TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad4, Smad3, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2, MyoD, Myf5, MyoG and MyHC relative mRNA levels. The levels of the myostatin-1 and myostatin-2 genes were downregulated, and the protein expression levels of p-Smad2, Smad2, Smad4, p-Akt, Akt, LARP6 and Smad3 were increased.
Conclusions: The appropriate levels of dietary protein promoted the growth of sub-adult grass carp and improved muscle hardness by promoting the growth of muscle fibers, improving collagen synthesis and depressing collagen degradation. In addition, the dietary protein requirements of sub-adult grass carp were 26.21% and 24.85% according to the quadratic regression analysis of growth performance (SGR) and the muscle hardness (collagen content), respectively.
Keywords: Collagen degradation; Collagen synthesis; Grass carp; Muscle fibers; Muscle hardness; Protein.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest should be disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dietary vitamin C improves muscle hardness and springiness associated with collagen and elastin synthesis in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella).Food Res Int. 2025 Aug;213:116591. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116591. Epub 2025 May 6. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40436569
-
A new insight on copper: Promotion of collagen synthesis and myofiber growth and development in juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella).Anim Nutr. 2023 Jul 8;15:22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.06.009. eCollection 2023 Dec. Anim Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37771856 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary effects of aucubin on growth and flesh quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) based on metabolomics.J Anim Sci. 2022 Oct 1;100(10):skac273. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac273. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35985277 Free PMC article.
-
The role of vitamin E in polyunsaturated fatty acid synthesis and alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress in sub-adult grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella).Anim Nutr. 2023 Dec 2;16:275-287. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.09.008. eCollection 2024 Mar. Anim Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38371478 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Paper Mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera) on Growth Performance and Muscle Quality of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella).Animals (Basel). 2021 Jun 2;11(6):1655. doi: 10.3390/ani11061655. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199491 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dietary supplementation with succinic acid improves growth performance and flesh quality of adult Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed a high-carbohydrate diet.Anim Nutr. 2024 May 25;18:390-407. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.04.016. eCollection 2024 Sep. Anim Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39309970 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of muscle quality in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with dietary faba bean (Vicia faba L.).Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 27;10:1153323. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1153323. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37051120 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Different Astaxanthin Sources on Fillet Coloration and Energy Deposition in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Aquac Nutr. 2024 Mar 25;2024:1664203. doi: 10.1155/2024/1664203. eCollection 2024. Aquac Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39555536 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Crude Protein and Lysine Levels Affect Meat Quality and Myofiber Characteristic of Slow-Growing Chicken.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jul 15;14(14):2068. doi: 10.3390/ani14142068. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061530 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Dietary Different Co-Forms of Lysine and Glutamate on Growth Performance, Muscle Development, Antioxidation and Related Gene Expressions in Juvenile Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus).Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2024 Feb;26(1):74-91. doi: 10.1007/s10126-023-10278-5. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2024. PMID: 38153607
References
-
- FAO . The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2020. Rome: Sustainability in action; 2020.
-
- NRC. Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. 2011th ed. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011.
-
- Xu J, Feng L, Jiang WD, Wu P, Liu Y, Jiang J, et al. Different dietary protein levels affect flesh quality, fatty acids and alter gene expression of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzymes in the muscle of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) Aquaculture. 2018;493:272–282. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.05.008. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2018YFD0900400/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2019YFD0900200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 31922086/National Outstanding Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32172988/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CARS-45/Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

