Plasma apolipoprotein E levels in longitudinally followed patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36002891
- PMCID: PMC9400269
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-022-01058-9
Plasma apolipoprotein E levels in longitudinally followed patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Low levels of plasma apolipoprotein E (apoE) and presence of the APOE ε4 allele are associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Although the increased risk of AD in APOE ε4-carriers is well-established, the protein levels have received limited attention.
Methods: We here report the total plasma apoE and apoE isoform levels at baseline from a longitudinally (24 months) followed cohort including controls (n = 39), patients with stable amnestic mild cognitive impairment during 24 months follow up (MCI-MCI, n = 30), patients with amnestic MCI (aMCI) that during follow-up were clinically diagnosed with AD with dementia (ADD) (MCI-ADD, n = 28), and patients with AD with dementia (ADD) at baseline (ADD, n = 28). We furthermore assessed associations between plasma apoE levels with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) AD biomarkers and α-synuclein, as well as both CSF and plasma neurofilament light chain (NfL), YKL-40 and kallikrein 6.
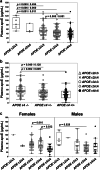
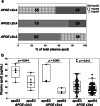
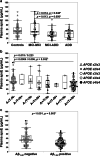
Results: Irrespective of clinical diagnosis, the highest versus the lowest apoE levels were found in APOE ε2/ε3 versus APOE ε4/ε4 subjects, with the most prominent differences exhibited in females. Total plasma apoE levels were 32% and 21% higher in the controls versus MCI-ADD and ADD patients, respectively. Interestingly, MCI-ADD patients exhibited a 30% reduction in plasma apoE compared to MCI-MCI patients. This decrease appeared to be associated with brain amyloid-β (Aβ42) pathology regardless of disease status as assessed using the Amyloid, Tau, and Neurodegeneration (A/T/N) classification. In addition to the association between low plasma apoE and low levels of CSF Aβ42, lower apoE levels were also related to higher levels of CSF total tau (t-tau) and tau phosphorylated at Threonine 181 residue (p-tau) and NfL as well as a worse performance on the mini-mental-state-examination. In MCI-ADD patients, low levels of plasma apoE were associated with higher levels of CSF α-synuclein and kallikrein 6. No significant correlations between plasma apoE and the astrocytic inflammatory marker YKL40 were observed.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate important associations between low plasma apoE levels, Aβ pathology, and progression from aMCI to a clinical ADD diagnosis.
Keywords: APOE ε4; Alzheimer’s disease; Apolipoprotein E; Mass spectrometry; Plasma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

