Bihemispheric developmental alterations in basal ganglia volumes following unilateral perinatal stroke
- PMID: 36002972
- PMCID: PMC9421529
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103143
Bihemispheric developmental alterations in basal ganglia volumes following unilateral perinatal stroke
Abstract
Introduction: Perinatal stroke affects millions of children and results in lifelong disability. Two forms prevail: arterial ischemic stroke (AIS), and periventricular venous infarction (PVI). With such focal damage early in life, neural structures may reorganize during development to determine clinical function, particularly in the contralesional hemisphere. Such processes are increasingly understood in the motor system, however, the role of the basal ganglia, a group of subcortical nuclei that are critical to movement, behaviour, and learning, remain relatively unexplored. Perinatal strokes that directly damage the basal ganglia have been associated with worse motor outcomes, but how developmental plasticity affects bilateral basal ganglia structure is unknown. We hypothesized that children with perinatal stroke have alterations in bilateral basal ganglia volumes, the degree of which correlates with clinical motor function.
Methods: Children with AIS or PVI, and controls, aged 6-19 years, were recruited from a population-based cohort. MRIs were acquired on a 3 T GE MR750w scanner. High-resolution T1-weighted images (166 slices, 1 mm isotropic voxels) underwent manual segmentations of bilateral caudate and putamen. Extracted volumes were corrected for total intracranial volume. A structure volume ratio quantified hemispheric asymmetry of caudate and putamen (non-dominant/dominant hemisphere structure volume) with ratios closer to 1 reflecting a greater degree of symmetry between structures. Participants were additionally dichotomized by volume ratios into two groups, those with values above the group mean (0.8) and those below. Motor function was assessed using the Assisting Hand Assessment (AHA) and the Box and Blocks test in affected (BBTA) and unaffected (BBTU) hands. Group differences in volumes were explored using Kruskal-Wallis tests, and interhemispheric differences using Wilcoxon. Partial Spearman correlations explored associations between volumes and motor function (factoring out age, and whole-brain white matter volume, a proxy for lesion extent).
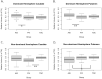
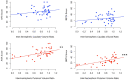
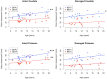
Results: In the dominant (non-lesioned) hemisphere, volumes were larger in AIS compared to PVI for both the caudate (p < 0.05) and putamen (p < 0.01) but comparable between stroke groups and controls. Non-dominant (lesioned) hemisphere volumes were larger for controls than AIS for the putamen (p < 0.05), and for the caudate in PVI (p = 0.001). Interhemispheric differences showed greater dominant hemisphere volumes for the putamen in controls (p < 0.01), for both the caudate (p < 0.01) and putamen (p < 0.001) in AIS, and for the caudate (p = 0.01) in PVI. Motor scores did not differ between AIS and PVI thus groups were combined to increase statistical power. Better motor scores were associated with larger non-dominant putamen volumes (BBTA: r = 0.40, p = 0.011), and larger putamen volume ratios (BBTA: r = 0.52, p < 0.001, AHA: r = 0.43, p < 0.01). For those with relatively symmetrical putamen volume ratios (ratio > group mean of 0.8), age was positively correlated with BBTA (r = 0.54, p < 0.01) and BBTU (r = 0.69, p < 0.001). For those with more asymmetrical putamen volume ratios, associations with motor function and age were not seen (BBTA: r = 0.21, p = 0.40, BBTU: r = 0.37, p = 0.13).
Conclusion: Specific perinatal stroke lesions affect different elements of basal ganglia development. PVI primarily affected the caudate, while AIS primarily affected the putamen. Putamen volumes in the lesioned hemisphere are associated with clinical motor function. The basal ganglia should be included in evolving models of developmental plasticity after perinatal stroke.
Keywords: Basal ganglia; Cerebral palsy; Motor function; Pediatric; Perinatal Stroke; Volumetrics.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ipsilesional volume loss of basal ganglia and thalamus is associated with poor hand function after ischemic perinatal stroke.BMC Neurol. 2022 Jan 12;22(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02550-3. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35022000 Free PMC article.
-
Thalamic diaschisis following perinatal stroke is associated with clinical disability.Neuroimage Clin. 2019;21:101660. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101660. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 30639178 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Remodelling of the Motor Cortex in Hemiparetic Children With Perinatal Stroke.Pediatr Neurol. 2020 Nov;112:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2020.08.004. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Pediatr Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32911261
-
The basal ganglia and apraxia.Brain. 1996 Feb;119 ( Pt 1):319-40. doi: 10.1093/brain/119.1.319. Brain. 1996. PMID: 8624692 Review.
-
Integrated technology for evaluation of brain function and neural plasticity.Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2004 Feb;15(1):263-306. doi: 10.1016/s1047-9651(03)00124-4. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2004. PMID: 15029909 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain growth until adolescence after a neonatal focal injury: sex related differences beyond lesion effect.Front Neurosci. 2024 Aug 23;18:1405381. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1405381. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39247049 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in cortical morphometry of the contralesional hemisphere in children, adolescents, and young adults with perinatal stroke.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 14;13(1):11391. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38185-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37452141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Harrach M., et al. Alterations in Cortical Morphology after Neonatal Stroke: Compensation in the Contralesional Hemisphere? Dev. Neurobiol. 2019;79:303–316. - PubMed
-
- Alexander G.E., DeLong M.R., Strick P.L. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1986;9:357–381. - PubMed
-
- Ashby F.G., Ennis J.M., Spiering B.J. A neurobiological theory of automaticity in perceptual categorization. Psychol. Rev. 2007;114:632–656. - PubMed
-
- Aylward E.H., et al. Basal Ganglia Volume and Proximity to Onset in Presymptomatic Huntington Disease. Arch. Neurol. 1996;53:1293–1296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

