Inborn errors of immunity associated with defects of thymic development
- PMID: 36003043
- PMCID: PMC11077434
- DOI: 10.1111/pai.13832
Inborn errors of immunity associated with defects of thymic development
Abstract
The main function of the thymus is to support the establishment of a wide repertoire of T lymphocytes capable of eliminating foreign pathogens, yet tolerant to self-antigens. Thymocyte development in the thymus is dependent on the interaction with thymic stromal cells, a complex mixture of cells comprising thymic epithelial cells (TEC), mesenchymal and endothelial cells. The exchange of signals between stromal cells and thymocytes is referred to as "thymic cross-talk". Genetic defects affecting either side of this interaction result in defects in thymic development that ultimately lead to a decreased output of T lymphocytes to the periphery. In the present review, we aim at providing a summary of inborn errors of immunity (IEI) characterized by T-cell lymphopenia due to defects of the thymic stroma, or to hematopoietic-intrinsic defects of T-cell development, with a special focus on recently discovered disorders. Additionally, we review the novel diagnostic tools developed to discover and study new genetic causes of IEI due to defects in thymic development. Finally, we discuss therapeutic approaches to correct thymic defects that are currently available, in addition to potential novel therapies that could be applied in the future.
Keywords: T-cell lymphopenia; immune deficiency; inborn errors of immunity; thymic development; thymic stroma; thymus.
Published 2022. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no financial conflict of interests.
Figures
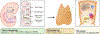
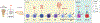
Similar articles
-
Thymic inborn errors of immunity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 Feb;155(2):368-376. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.10.009. Epub 2024 Oct 18. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39428079 Review.
-
Human thymus in health and disease: Recent advances in diagnosis and biology.Semin Immunol. 2023 Mar;66:101732. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101732. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Semin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36863139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inborn errors of thymic stromal cell development and function.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Feb;43(1):85-100. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00826-9. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 33257998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and Future Therapeutic Approaches for Thymic Stromal Cell Defects.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 18;12:655354. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.655354. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33815417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokines in the thymus: production and biological effects.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Feb;11(4):447-64. doi: 10.2174/0929867043455972. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 14965226 Review.
Cited by
-
Rediscovering the human thymus through cutting-edge technologies.J Exp Med. 2024 Oct 7;221(10):e20230892. doi: 10.1084/jem.20230892. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39167072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary and secondary defects of the thymus.Immunol Rev. 2024 Mar;322(1):178-211. doi: 10.1111/imr.13306. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38228406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymic inborn errors of immunity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 Feb;155(2):368-376. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.10.009. Epub 2024 Oct 18. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39428079 Review.
-
IL-7-dependent and -independent lineages of IL-7R-dependent human T cells.J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 1;134(19):e180251. doi: 10.1172/JCI180251. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39352394 Free PMC article.
-
A guide to thymic selection of T cells.Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Feb;24(2):103-117. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00911-8. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37464188 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

