Cord blood IgE predicts allergic sensitization, elevation of exhaled nitric oxide, and asthma in schoolchildren
- PMID: 36003048
- PMCID: PMC9541746
- DOI: 10.1111/pai.13838
Cord blood IgE predicts allergic sensitization, elevation of exhaled nitric oxide, and asthma in schoolchildren
Abstract
Background: Few data are available in Asian children regarding the validity of cord blood immunoglobulin E (IgE) in predicting allergic sensitization and pulmonary function. The relationship between cord blood IgE and fraction of exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) remains unknown. This study investigated the associations of cord blood IgE with allergic sensitization, FeNO, pulmonary function, and allergic diseases in Asian children.
Methods: Five hundred and sixty-six Asian children with valid cord blood IgE measurements at birth participated a 6-year follow-up visit including a questionnaire, serum total and allergen-specific IgE, FeNO measurement, and spirometry. Regression-based analyses with covariates adjustment were applied.
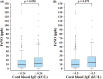
Results: Cord blood IgE levels were significantly associated with FeNO levels (β = 0.131, p < .001) and serum total IgE levels (β = 0.325, p < .001). Cord blood IgE levels were positively associated with allergic sensitization (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 2.22, p < .001), and sensitization to mites (p = .002), animals (p = .023), and foods (p = .048). Subjects with cord blood IgE ≥0.24 kU/L (the optimal cutoff) were significantly associated with an increased risk of allergic sensitization (AOR = 2.63, p < .001) and asthma (AOR = 2.35, p = .024) than those with cord blood IgE <0.24 kU/L. Subjects with cord blood IgE ≥0.24 kU/L had significantly higher FeNO levels than those with cord blood IgE <0.24 kU/L (p = .028). There were no significant associations between cord blood IgE levels and pulmonary function parameters.
Conclusion: Cord blood IgE ≥0.24 kU/L predicts allergic sensitization, FeNO elevation, and asthma among Asian schoolchildren, suggesting cord blood IgE would be useful for identifying newborns at risk of subsequent allergic sensitization and allergic airway inflammation.
Keywords: allergic sensitization; asthma; cord blood IgE; exhaled nitric oxide; pulmonary function.
© 2022 The Authors. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Allergen exposure modifies the relation of sensitization to fraction of exhaled nitric oxide levels in children at risk for allergy and asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 May;127(5):1165-72.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.01.066. Epub 2011 Apr 3. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21463890 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of exhaled nitric oxide levels (FeNO) in childhood atopic asthma: evidence for neonatal respiratory distress as a factor associated with low FeNO levels.J Asthma. 2010 Sep;47(7):810-6. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2010.489245. J Asthma. 2010. PMID: 20626311
-
IgE sensitization to food allergens and airborne allergens in relation to biomarkers of type 2 inflammation in asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2018 Sep;48(9):1147-1154. doi: 10.1111/cea.13165. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Clin Exp Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29746003
-
Fractional exhaled nitric oxide measurements are most closely associated with allergic sensitization in school-age children.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009 Nov;124(5):949-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.07.024. Epub 2009 Sep 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19748661 Free PMC article.
-
Low-grade disease activity in early life precedes childhood asthma and allergy.Dan Med J. 2016 Aug;63(8):B5272. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27477800 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between telomere length and atopic dermatitis among school-age children.Clin Transl Allergy. 2025 Jun;15(6):e70066. doi: 10.1002/clt2.70066. Clin Transl Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40437344 Free PMC article.
-
Basophils Predict Mite Sensitization in Patients with Kawasaki Disease.Children (Basel). 2023 Jul 12;10(7):1209. doi: 10.3390/children10071209. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508706 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary function in school-age children following intravitreal injection of bevacizumab for retinopathy of prematurity.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 5;12(1):18788. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22338-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36335152 Free PMC article.
-
Early Prediction of Asthma.J Clin Med. 2023 Aug 20;12(16):5404. doi: 10.3390/jcm12165404. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37629446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of advanced paternal age with lung function at school age.Respir Res. 2022 Sep 20;23(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02178-4. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 36127724 Free PMC article.

