Analysis of school support: Systematic literature review of core Chinese- and English-language journals published in 2000-2021
- PMID: 36003103
- PMCID: PMC9393531
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.933695
Analysis of school support: Systematic literature review of core Chinese- and English-language journals published in 2000-2021
Abstract
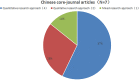
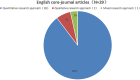
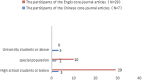
School support is of great significance to students' academic quality and overall physical and psychological development. However, there is still ambiguity in the English and Chinese studies on the concept and measurement tools of school support. The data for this study were sourced from the literature on school support included in the China National Knowledge Network (CNKI) and Web of Science (WOS) from 2000 to 2021. A systematic literature review was conducted through literature inclusion and data extraction according to the PRISMA guidelines. Finally, 36 core-journal articles with high academic reference value and authority are identified, including seven in Chinese and 29 in English. The following results were obtained: (1) Related research in both Chinese and English showed an overall increasing trend. (2) The concepts and measurement tools of school support were not clear, and most studies used concepts and measurement tools of "social support" or "school climate" as substitutes for school support. (3) Most of the previous studies were based on social support theory, ecological system theory, and school climate theory. (4) The research mainly adopts quantitative research methods and focuses on special student populations or students below the high school level. Overall, previous studies indicated that school support has a positive impact on student development. Therefore, future research should be broadly extended to the knowledge system in higher education. On the basis of clarifying the concept of school support, it is necessary to try to develop and validate school support measurement tools with great reliability, validity, and general applicability to provide a practical reference for educators around the world.
Keywords: articles; definition; measurement tools; school support; systematic literature review.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Hu and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
The effectiveness of web-based programs on the reduction of childhood obesity in school-aged children: A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-14. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-248. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820152
-
The relationship between school climate and students' non-cognitive skills: A systematic literature review.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 23;9(4):e14773. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14773. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37025858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Out-of-school settings as a developmental context for children and youth.Adv Child Dev Behav. 2005;33:43-77. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2407(05)80004-7. Adv Child Dev Behav. 2005. PMID: 16101114
-
Interventions in Chinese Undergraduate Students' Mental Health: Systematic Review.Interact J Med Res. 2022 Jun 15;11(1):e38249. doi: 10.2196/38249. Interact J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35704383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson-Butcher D., Amorose A. J., Iachini A., Ball A. (2013). Community and Youth Collaborative Institute School Experience Surveys. Columbus, OH: College of Social Work, The Ohio State University.
-
- Arslan G. (2018). Social exclusion, social support and psychological wellbeing at school: a study of mediation and moderation effect. Child Indicat. Res. 11, 897–918. 10.1007/s12187-017-9451-1 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

