The role of C5a-C5aR1 axis in bone pathophysiology: A mini-review
- PMID: 36003145
- PMCID: PMC9393612
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.957800
The role of C5a-C5aR1 axis in bone pathophysiology: A mini-review
Abstract
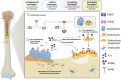
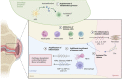
Bone remodeling is a physiological, dynamic process that mainly depends on the functions of 2 cell types: osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Emerging evidence suggests that complement system is crucially involved in the regulation of functions of these cells, especially during inflammatory states. In this context, complement component 5a (C5a), a powerful pro-inflammatory anaphylatoxin that binds the receptor C5aR1, is known to regulate osteoclast formation and osteoblast inflammatory responses, and has thus been proposed as potential therapeutic target for the treatment of inflammatory bone diseases. In this review, we will analyze the role of C5a-C5aR1 axis in bone physiology and pathophysiology, describing its involvement in the pathogenesis of some of the most frequent inflammatory bone diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, and also in osteoporosis and bone cancer and metastasis. Moreover, we will examine C5aR1-based pharmacological approaches that are available and have been tested so far for the treatment of these conditions. Given the growing interest of the scientific community on osteoimmunology, and the scarcity of data regarding the role of C5a-C5aR1 axis in bone pathophysiology, we will highlight the importance of this axis in mediating the interactions between skeletal and immune systems and its potential use as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: C5a; C5aR1; bone; osteoblasts; osteoclasts; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Ruocco, Sirico, Novelli, Iannelli, Van Breda, Kyburz, Hasler, Aramini and Amendola.
Conflict of interest statement
AR, AS, RN, SI, AA, and PA are employees of Dompé Farmaceutici SpA. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ajona D., Ortiz-Espinosa S., Moreno H., Lozano T., Pajares M. J., Agorreta J., et al. (2017). A combined PD-1/C5a blockade synergistically protects against lung cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Discov. 7 (7), 694–703. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1184 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ajona D., Zandueta C., Corrales L., Moreno H., Pajares M. J., Ortiz-Espinosa S., et al. (2018). Blockade of the complement C5a/C5aR1 axis impairs lung cancer bone metastasis by CXCL16-mediated effects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 197 (9), 1164–1176. 10.1164/rccm.201703-0660OC - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ajona D., Zandueta C., Corrales L., Moreno H., Pajares M. J., Ortiz-Espinosa S., et al. (2018). Blockade of the complement C5a/C5aR1 Axis impairs lung cancer bone metastasis by CXCL16-mediated effects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 197 (9), 1164–1176. 10.1164/rccm.201703-0660OC - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ames R. S., Lee D., Foley J. J., Jurewicz A. J., Tornetta M. A., Bautsch W., et al. (2001). Identification of a selective nonpeptide antagonist of the anaphylatoxin C3a receptor that demonstrates antiinflammatory activity in animal models. J. Immunol. 166 (10), 6341–6348. 10.4049/jimmunol.166.10.6341 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

