Prognostic value of SOX9 in cervical cancer: Bioinformatics and experimental approaches
- PMID: 36003340
- PMCID: PMC9394184
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.939328
Prognostic value of SOX9 in cervical cancer: Bioinformatics and experimental approaches
Abstract
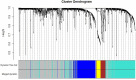
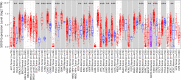
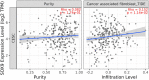
Among gynecological cancers, cervical cancer is a common malignancy and remains the leading cause of cancer-related death for women. However, the exact molecular pathogenesis of cervical cancer is not known. Hence, understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying cervical cancer pathogenesis will aid in the development of effective treatment modalities. In this research, we attempted to discern candidate biomarkers for cervical cancer by using multiple bioinformatics approaches. First, we performed differential expression analysis based on cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma data from The Cancer Genome Atlas database, then used differentially expressed genes for weighted gene co-expression network construction to find the most relevant gene module for cervical cancer. Next, the Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analyses were performed on the module genes, followed by using protein-protein interaction network analysis and Cytoscape to find the key gene. Finally, we validated the key gene by using multiple online sites and experimental methods. Through weighted gene co-expression network analysis, we found the turquoise module was the highest correlated module with cervical cancer diagnosis. The biological process of the module genes focused on cell proliferation, cell adhesion, and protein binding processes, while the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway of the module significantly enriched pathways related to cancer and cell circle. Among the module genes, SOX9 was identified as the hub gene, and its expression was associated with cervical cancer prognosis. We found the expression of SOX9 correlates with cancer-associated fibroblast immune infiltration in immune cells by Timer2.0. Furthermore, cancer-associated fibroblast infiltration is linked to cervical cancer patients' prognosis. Compared to those in normal adjacent, immunohistochemical and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) showed that the protein and mRNA expression of SOX9 in cervical cancer were higher. Therefore, the SOX9 gene acts as an oncogene in cervical cancer, interactive with immune infiltration of cancer-associated fibroblasts, thereby affecting the prognosis of patients with cervical cancer.
Keywords: bioinformatics; cancer-related fibroblasts; cervical cancer; differentially expressed genes (DEGs); hub gene; weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA).
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Chen, Zeng, Fu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Ashrafizadeh M., Zarrabi A., Orouei S., Zabolian A., Saleki H., Azami N., et al. (2021). Interplay between SOX9 transcription factor and microRNAs in cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 183, 681–694. Epub 2021 May 3. PMID: 33957202. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.185 PubMed Abstract | 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.185 | Google Scholar - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson H., Ray A., Spellman P., Speed T. P. (2009). A single-sample method for normalizing and combining full-resolution copy numbers from multiple platforms, labs and analysis methods. Bioinformatics 25 (7), 861–867. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp074 PubMed Abstract | 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp074 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burnichon N., Buffet A., Parfait B., Letouze E., Laurendeau I., Loriot C., et al. (2012). Somatic NF1 inactivation is a frequent event in sporadic pheochromocytoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21 (26), 5397–5405. 10.1093/hmg/dds374 PubMed Abstract | 10.1093/hmg/dds374 | Google Scholar - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cai C., Wang H., He H. H., Chen S., He L., Ma F., et al. (2013). ERG induces androgen receptor-mediated regulation of SOX9 in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 123 (3), 1109–1122. 10.1172/JCI66666 PubMed Abstract | 10.1172/JCI66666 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang C. V., Araujo R. V., Cirqueira C. S., Cani C. M., Matushita H., Cescato V. A., et al. (2017). Differential expression of stem cell markers in human adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma and pituitary adenoma. Neuroendocrinology 104 (2), 183–193. 10.1159/000446072 PubMed Abstract | 10.1159/000446072 | Google Scholar - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

