Inhibition of PCSK9 enhances the antitumor effect of PD-1 inhibitor in colorectal cancer by promoting the infiltration of CD8+ T cells and the exclusion of Treg cells
- PMID: 36003387
- PMCID: PMC9393481
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947756
Inhibition of PCSK9 enhances the antitumor effect of PD-1 inhibitor in colorectal cancer by promoting the infiltration of CD8+ T cells and the exclusion of Treg cells
Abstract
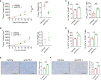
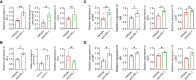
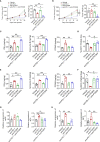
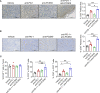
Immunotherapy especially immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has brought favorable clinical results for numerous cancer patients. However, the efficacy of ICIs in colorectal cancer (CRC) is still unsatisfactory due to the poor median progression-free survival and overall survival. Here, based on the CRC models, we tried to elucidate novel relapse mechanisms during anti-PD-1 therapy. We found that PD-1 blockade elicited a mild antitumor effect in these tumor models with both increased CD8+ T cells and Treg cells. Gene mapping analysis indicated that proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), low-density lipoprotein receptor, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), and CD36 were unexpectedly upregulated during PD-1 blockade. To investigate the critical role of these proteins especially PCSK9 in tumor growth, anti-PCSK9 antibody in combination with anti-PD-1 antibody was employed to block PCSK9 and PD-1 simultaneously in CRC. Data showed that neutralizing PCSK9 during anti-PD-1 therapy elicited a synergetic antitumor effect with increased CD8+ T-cell infiltration and inflammatory cytokine releases. Moreover, the proportion of Treg cells was significantly reduced by co-inhibiting PCSK9 and PD-1. Overall, inhibiting PCSK9 can further enhance the antitumor effect of anti-PD-1 therapy in CRC, indicating that targeting PCSK9 could be a promising approach to potentiate ICI efficacy.
Keywords: CD8+ T cells; PCSK9; PD-1; regulatory T cells; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Liu, He, An, Guo, Zhang and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

