DIA proteomics identified the potential targets associated with angiogenesis in the mammary glands of dairy cows with hemorrhagic mastitis
- PMID: 36003411
- PMCID: PMC9393364
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.980963
DIA proteomics identified the potential targets associated with angiogenesis in the mammary glands of dairy cows with hemorrhagic mastitis
Abstract
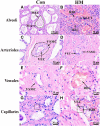
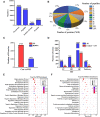
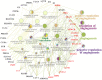
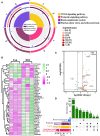
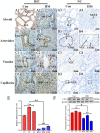
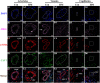
Hemorrhagic mastitis (HM) in dairy cows caused great economic losses in the dairy industry due to decreased milk production and increased costs associated with cattle management and treatment. However, the pathological and molecular mechanisms of HM are not well-understood. The present study aimed to investigate differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) associated with HM according to data-independent acquisition (DIA) proteomics. Compared to the mammary glands of healthylactating Holstein cows (Control, C group), the pathology of the HM group displayed massive alveolar infiltration of hemocytes and neutrophils, and the blood vessels, including arteriole, venules and capillaries were incomplete and damaged, with a loss of endothelial cells. DIA proteomics results showed that a total of 3,739 DEPs and 819 biological process terms were screened in the HM group. We focused on the blood, permeability of blood vessel, vascular and angiogenesis of mammary glands, and a total of 99 candidate DEPs, including 60 up- and 39 down-regulated DEPs, were obtained from the Gene Ontology (GO) and Pathway enrichment analyses. Phenotype prediction and function analysis of the DEPs revealed that three DEPs, particularly Caveolin-1(CAV1), were participated in the regulation of angiogenesis. Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence staining showed that the CAV1 protein was present mainly in the mammary epithelial cells, vascular endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells. The expression level of CAV1 mRNA and protein in the HM group was significantly down-regulated. The results will be helpful to the further understanding of the pathological and molecular mechanisms of HM in dairy cows.
Keywords: CAV1; DIA proteomics; angiogenesis; blood and cow; hemorrhagic mastitis.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Bai, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Dai, Lin, Gao, Zhang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kurt S, Funda EK. Pathogen isolation and antibiogram analysis in dairy cows with clinical mastitis in adana region, Turkey. Etlik Vet Mikrob Dergisi. (2021) 32:20–26. 10.35864/evmd.906990 - DOI
-
- Kabera F, Roy JP, Afifi M, Godden S, Dufour S. Comparing blanket vs. selective dry cow treatment approaches for elimination and prevention of intramammary infections during the dry period: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Vet Sci. (2021) 8:688450. 10.3389/fvets.2021.688450 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cifrian E, Guidry AJ, Bramley AJ, Norcross NL, Bastida-Corcuera FD, Marquardt WW. Effect of staphylococcal beta toxin on the cytotoxicity, proliferation and adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to bovine mammary epithelial cells. Vet Microbiol. (1996) 48:187–98. 10.1016/0378-1135(95)00159-X - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

