Exosome derived from stem cell: A promising therapeutics for wound healing
- PMID: 36003496
- PMCID: PMC9395204
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.957771
Exosome derived from stem cell: A promising therapeutics for wound healing
Abstract
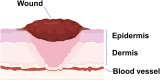
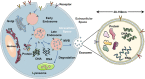
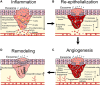
A wound occurs when the epidermis and dermis of the skin are damaged internally and externally. The traditional wound healing method is unsatisfactory, which will prolong the treatment time and increase the treatment cost, which brings economic and psychological burdens to patients. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a new method to accelerate wound healing. As a cell-free therapy, exosome derived from stem cell (EdSC) offers new possibilities for wound healing. EdSC is the smallest extracellular vesicle secreted by stem cells with diameters of 30-150 nm and a lipid bilayer structure. Previous studies have found that EdSC can participate in and promote almost all stages of wound healing, including regulating inflammatory cells; improving activation of fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and endothelial cells; and adjusting the ratio of collagen Ⅰ and Ⅲ. We reviewed the relevant knowledge of wounds; summarized the biogenesis, isolation, and identification of exosomes; and clarified the pharmacological role of exosomes in promoting wound healing. This review provides knowledge support for the pharmacological study of exosomes.
Keywords: exosome; stem cell; therapeutics; wound; wound healing.
Copyright © 2022 Lv, Liu, Sun, Wang, Zhang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Al Gailani M., Liu M., Wen J. (2022). Ligands for oral delivery of peptides across the blood-brain-barrier. Acta Mater. Medica 1, 1. 10.15212/amm-2021-0007 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

