The efficacy and safety of dachaihu decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36003504
- PMCID: PMC9393237
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.918681
The efficacy and safety of dachaihu decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
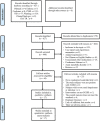
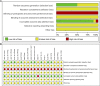
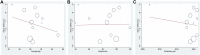
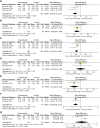
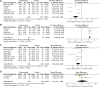
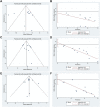
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a clinical metabolic syndrome characterized by persistent hyperglycemia, which is caused by defective insulin secretion and decreased function in regulating glucose metabolism. Dachaihu Decoction (DCHD) is a traditional Chinese medicine formula that has been gradually used in T2DM treatment. A comprehensive analysis on the efficacy and safety of DCHD in T2DM treatment is necessary. Objective: This meta-analysis aimed to systematically assess the clinical efficacy and safety of DCHD in the T2DM treatment and provide a reference for subsequent research and clinical practice. Methods: Both Chinese and English databases were searched from their inceptions to November 2021. All retrieved studies were screened according to inclusion and exclusion criteria and randomized controlled trials about DCHD on T2DM were enrolled. The quality of the literature was assessed using the bias risk assessment tool in the Cochrane Handbook. Data extraction was performed on the selected studies. Review Manager 5.4 and Stata 16.0 were used for meta-analysis. Sources of heterogeneity were also explored by using meta-regression and subgroup analysis. Funnel plot and Egger's test were used to assess publication bias and the evidence quality was assessed by GRADE. Results: 17 eligible studies, involving 1,525 patients, were included in this study. Compared with conventional treatment, combined treatment with DCHD was significantly better in improving HbA1c (MD = -0.90%, 95%CI: -1.20 to -0.60, p < 0.01), FBG (MD = -1.08 mmol/L, 95%CI: -1.28 to -0.87, p < 0.01), 2hPG (MD = -1.25 mmol/L, 95%CI: -1.42 to -1.09, p < 0.01), TC (MD = -0.50 mmol/L, 95%CI: -0.70 to -0.30, p < 0.01), TG (MD = -0.44 mmol/L, 95%CI: -0.61 to -0.26, p < 0.01), LDL-C (MD = -0.58 mmol/L, 95%CI: -0.85 to -0.31, p < 0.01), HOMA-IR (SMD = -2.04, 95%CI: -3.09 to -0.99, p < 0.01), HOMA-β (SMD = 2.48, 95%CI: 2.20 to 2.76, p < 0.01) and BMI (MD = -1.52 kg/m2, 95%CI: -2.55 to -0.49, p < 0.01). When DCHD used alone, it had a similar efficacy to conventional treatment in HbA1c (MD = -0.04%, 95%CI: -0.17 to 0.09, p = 0.57) and FBG (MD = 0.13 mmol/L, 95%CI: -0.09 to 0.36, p = 0.24). It can also reduce 2hPG, even if not as effective as conventional treatment (MD = 0.54 mmol/L, 95%CI: 0.19 to 0.89, p < 0.01). Due to the small number of included studies, it is unclear whether DCHD used alone has an improving effect on lipid metabolism, BMI, HOMA-IR and HOMA-β. Analysis of adverse events showed DCHD was relatively safe. No obvious publication bias was detected by Funnel plot and Egger's test. Conclusion: Based on this meta-analysis, we found that the combination with DCHD in the T2DM treatment has more advantages than conventional treatment alone, which can further regulate the glucose and lipid metabolism, reduce insulin resistance, improve islet function and lower BMI. DCHD alone also plays a certain role in regulating glucose. Meanwhile, DCHD is relatively safe. However, limited by the quality and quantity of included studies, the efficacy and safety of DCHD remain uncertain. More high-quality studies are still needed to provide more reliable evidence for the clinical application of DCHD. Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42021296718, identifier CRD42021296718.
Keywords: dachaihu decoction; meta-analysis; systematic review; traditional Chinese medicine; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Leng, Fu, Yang, Xie, Yuan, Liang, Gao and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The efficacy and safety of Dachaihu decoction in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 2;11:1397900. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1397900. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39015790 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine as an add-on therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with carotid atherosclerosis: An updated meta-analysis of 27 randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 23;14:1091718. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1091718. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37033624 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Gegen Qinlian decoction in the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 26;14:1316269. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1316269. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38344688 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves extract combined with ACEI/ARB on diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 41 randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 3;15:1408546. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1408546. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39830333 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of qiwei baizhu san in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1501990. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1501990. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39845797 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chronic Atopic Dermatitis with Eosinophilia Improved by Daesiho-Tang: A Case Report.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Sep 20;16:2561-2572. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S424225. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37750085 Free PMC article.
-
Dachaihu decoction inhibits hypernutrition-induced liver metastasis from colorectal cancer by maintaining the gut vascular barrier.Cancer Pathog Ther. 2023 Mar 7;1(2):98-110. doi: 10.1016/j.cpt.2023.02.003. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cancer Pathog Ther. 2023. PMID: 38328407 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Dachaihu decoction in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 2;11:1397900. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1397900. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39015790 Free PMC article.
-
Single Herbal Medicine for Insulin Resistance: Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Jun 10;14:e68915. doi: 10.2196/68915. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40493913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao W. P., Fan Y. F., Chu X. Q. (2020). Efficiency observation of dachaihu decoction and exenatide on newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by non-alcoholic fatty liver. Shanxi J. TCM 36 (2), 27–29.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

