Allyl methyl trisulfide protected against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via inhibition of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways
- PMID: 36003507
- PMCID: PMC9394683
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.919898
Allyl methyl trisulfide protected against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via inhibition of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways
Abstract
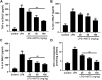
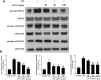
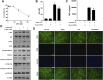
Allyl methyl trisulfide (AMTS) is one major lipid-soluble organosulfur compound of garlic. Previous studies have reported the potential therapeutic effect of garlic on acute lung injury (ALI) or its severe condition acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), but the specific substances that exert the regulatory effects are still unclear. In this study, we investigate the protective effects of AMTS on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI mice and explored the underlying mechanisms. In vivo experiments, ICR mice were pretreated with 25-100 mg/kg AMTS for 7 days and followed by intratracheal instillation of LPS (1.5 mg/kg). The results showed that AMTS significantly attenuated LPS-induced deterioration of lung pathology, demonstrated by ameliorative edema and protein leakage, and improved pulmonary histopathological morphology. Meanwhile, the expression of inflammatory mediators and the infiltration of inflammation-regulation cells induced by LPS were also inhibited. In vitro experiments also revealed that AMTS could alleviate inflammation response and inhibit the exaggeration of macrophage M1 polarization in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Mechanistically, we identified that AMTS treatment could attenuate the LPS-induced elevation of protein expression of p-IκBα, nuclear NF-κB-p65, COX2, iNOS, p-P38, p-ERK1/2, and p-JNK. Collectively, these data suggest that AMTS could attenuate LPS-induced ALI and the molecular mechanisms should be related to the suppression of the NF-κB and MAPKs pathways.
Keywords: NF-κB; acute lung injury; allyl methyl trisulfide; inflammatory mediators; mapks.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Liu, Dong, Fan, Wang, Wu, Li, Kou and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
S-allylmercaptocysteine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via nuclear factor kappa B and Keap1/Nrf2 pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Apr;81:106273. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106273. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32070920
-
LincRNA-p21 promotes classical macrophage activation in acute respiratory distress syndrome by activating NF-κB.Exp Lung Res. 2020 May-Aug;46(6):174-184. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2020.1758246. Epub 2020 May 2. Exp Lung Res. 2020. PMID: 32362153
-
Kaempferol regulates MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways to attenuate LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2012 Oct;14(2):209-16. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2012.07.007. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22835426
-
LFG-500, a newly synthesized flavonoid, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and inflammation in mice.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 1;113:57-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.05.007. Epub 2016 May 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27206337
-
Methanol extract of Antrodia camphorata protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways in mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Jun 11;62(23):5321-9. doi: 10.1021/jf405113g. Epub 2014 May 29. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24849405
Cited by
-
Valsartan attenuates LPS-induced ALI by modulating NF-κB and MAPK pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 15;15:1321095. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1321095. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38288441 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage‑driven pathogenesis in acute lung injury/acute respiratory disease syndrome: Harnessing natural products for therapeutic interventions (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jan;31(1):16. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13381. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39513609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isostrictiniin Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via the Regulation of the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 and MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 19;26(12):5912. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125912. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565375 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary supplementation of wild leek (Allium tricoccum) and garlic (Allium sativum) leaves on production, egg quality, serum lipid profile, intestinal morphology and nutrient digestibility of laying quails.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2024 Jul 27;56(7):224. doi: 10.1007/s11250-024-04090-z. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2024. PMID: 39066801
-
Echinatin attenuates acute lung injury and inflammatory responses via TAK1-MAPK/NF-κB and Keap1-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathways in macrophages.PLoS One. 2024 May 16;19(5):e0303556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303556. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38753858 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

