Hearing loss and its associated factors among metal workshop workers at Gondar city, Northwest Ethiopia
- PMID: 36003635
- PMCID: PMC9393372
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.919239
Hearing loss and its associated factors among metal workshop workers at Gondar city, Northwest Ethiopia
Abstract
Introduction: Noise-induced hearing loss is a permanent sensorineural deficiency, which is caused by exposure to excessive noise sound. Although noise-induced hearing loss due to industrialization is a main public health problem in Ethiopia, studies on the prevalence and associated factors of hearing loss are scarce.
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the prevalence and associated factors of hearing loss among workers at a metal workshop in Gondar city, Northwest Ethiopia.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was employed among 300 participants using a stratified sampling technique. Data were collected using an interviewer-administered questionnaire. Bivariable and multivariable logistic regressions were conducted. In the multivariable logistic regression model, adjusted odds ratios (AOR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) and a p < 0.05 were computed to determine the level of significance.
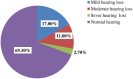
Results: The prevalence of hearing loss among metal workshop workers was 30.7% [95% CI: (25.7, 35.7)]. Age between 30 and 44 years [AOR = 2.9; 95% CI: 1.2, 7.1], age between 45 and 65 years [AOR = 3.8; 95% CI (1.5, 9.5)], cigarette smoking [AOR = 2.3; 95% CI: 1.2, 4.5], working area noise level >85 dB [AOR = 2.2; 95% CI: 1.1, 6.5], working experience of 6-10 years [AOR = 1.8; 95% CI: 1.4, 6.0], working experience >10 years [AOR = 3.5; 95% CI: 1.3, 4.3], and using ear protection devices [AOR = 0.3; 95% CI: 0.1, 0.6] were significantly associated with hearing loss.
Conclusion: The prevalence of hearing loss was considerably high. This study revealed that advanced age, cigarette smoking, increased working area noise level, and working experiences were found to increase the odds of having hearing loss. Therefore, it is important to emphasize metal workshop workers that are at high risk of hearing loss and develop preventive strategies to reduce the burden of this problem. Besides, minimizing working area noise levels, proper utilization of ear protection devices, and creating awareness about the impact of hearing loss are recommended.
Keywords: Gondar city; associated factors; audiometer; hearing loss; metalworkers.
Copyright © 2022 Melese, Adugna, Mulat and Adera.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer BF declared a shared affiliation with the authors DA, MM, AA, and BM to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous