Research progress on the relationship between autophagy and chronic complications of diabetes
- PMID: 36003645
- PMCID: PMC9393249
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.956344
Research progress on the relationship between autophagy and chronic complications of diabetes
Abstract
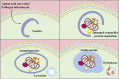
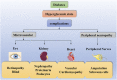
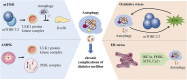
Diabetes is a common metabolic disease whose hyperglycemic state can induce diverse complications and even threaten human health and life security. Currently, the treatment of diabetes is restricted to drugs that regulate blood glucose and have certain accompanying side effects. Autophagy, a research hotspot, has been proven to be involved in the occurrence and progression of the chronic complications of diabetes. Autophagy, as an essential organismal defense mechanism, refers to the wrapping of cytoplasmic proteins, broken organelles or pathogens by vesicles, which are then degraded by lysosomes to maintain the stability of the intracellular environment. Here, we review the relevant aspects of autophagy and the molecular mechanisms of autophagy in diabetic chronic complications, and further analyze the impact of improving autophagy on diabetic chronic complications, which will contribute to a new direction for further prevention and treatment of diabetic chronic complications.
Keywords: autophagy; chronic complications; diabetes drug; molecular mechanism; regulation.
Copyright © 2022 Ge, Wang, Fei, Ye and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

