Development and validation of a nomogram to predict kidney survival at baseline in patients with C3 glomerulopathy
- PMID: 36003665
- PMCID: PMC9394716
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfac108
Development and validation of a nomogram to predict kidney survival at baseline in patients with C3 glomerulopathy
Abstract
Background: C3 glomerulopathy is a rare and heterogeneous complement-driven disease. It is often challenging to accurately predict in clinical practice the individual kidney prognosis at baseline. We herein sought to develop and validate a prognostic nomogram to predict long-term kidney survival.
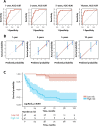
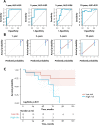
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, multicenter observational cohort study in 35 nephrology departments belonging to the Spanish Group for the Study of Glomerular Diseases. The dataset was randomly divided into a training group (n = 87) and a validation group (n = 28). The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was used to screen the main predictors of kidney outcome and to build the nomogram. The accuracy of the nomogram was assessed by discrimination and risk calibration in the training and validation sets.
Results: The study group comprised 115 patients, of whom 46 (40%) reached kidney failure in a median follow-up of 49 months (range 24-112). No significant differences were observed in baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), proteinuria or total chronicity score of kidney biopsies, between patients in the training versus those in the validation set. The selected variables by LASSO were eGFR, proteinuria and total chronicity score. Based on a Cox model, a nomogram was developed for the prediction of kidney survival at 1, 2, 5 and 10 years from diagnosis. The C-index of the nomogram was 0.860 (95% confidence interval 0.834-0.887) and calibration plots showed optimal agreement between predicted and observed outcomes.
Conclusions: We constructed and validated a practical nomogram with good discrimination and calibration to predict the risk of kidney failure in C3 glomerulopathy patients at 1, 2, 5 and 10 years.
Keywords: C3 glomerulopathy; calibration; discrimination; kidney failure; nomogram.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures



References
-
- Caravaca-Fontán F, Lucientes L, Cavero T, Praga M.. Update on C3 glomerulopathy: a complement-mediated disease. Nephron 2020; 144: 272–280 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad SB, Bomback AS. C3 glomerulopathy: pathogenesis and treatment. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2020; 27: 104–110 - PubMed
-
- Caravaca-Fontán F, Trujillo H, Alonso Met al. . Validation of a histologic scoring index for C3 glomerulopathy. Am J Kidney Dis 2021; 77: 684–695.e1 - PubMed
-
- Bomback AS, Santoriello D, Avasare RSet al. . C3 glomerulonephritis and dense deposit disease share a similar disease course in a large United States cohort of patients with C3 glomerulopathy. Kidney Int 2018; 93: 977–985 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

