Circulating inflammatory cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: Implications for treatment
- PMID: 36003772
- PMCID: PMC9393759
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.882896
Circulating inflammatory cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: Implications for treatment
Abstract
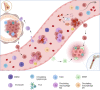
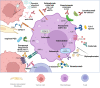
Adaptive and innate immune cells play a crucial role as regulators of cancer development. Inflammatory cells in blood flow seem to be involved in pro-tumor activities and contribute to breast cancer progression. Circulating lymphocyte ratios such as the platelet-lymphocytes ratio (PLR), the monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) and the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) are new reproducible, routinely feasible and cheap biomarkers of immune response. These indexes have been correlated to prognosis in many solid tumors and there is growing evidence on their clinical applicability as independent prognostic markers also for breast cancer. In this review we give an overview of the possible value of lymphocytic indexes in advanced breast cancer prognosis and prediction of outcome. Furthermore, targeting the immune system appear to be a promising therapeutic strategy for breast cancer, especially macrophage-targeted therapies. Herein we present an overview of the ongoing clinical trials testing systemic inflammatory cells as therapeutic targets in breast cancer.
Keywords: NLR; biomarker; inflammatory cells; macrophages; metastatic breast cancer; new treatments; predictive; prognostic.
Copyright © 2022 Gianni, Palleschi, Schepisi, Casadei, Bleve, Merloni, Sirico, Sarti, Cecconetto, Di Menna, Schettini and De Giorgi.
Conflict of interest statement
This research received no external funding. MP has received advisory board fees from Novartis. UD has received advisory board or consultant fees from Merck Sharp and Dohme, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Astellas, Sanofi, Bayer, Pfizer, Ipsen, Novartis, and Pharmamar and institutional research grants from Astrazeneca, Sanofi, and Roche. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A high neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio are associated with a worse outcome in inflammatory breast cancer.Breast. 2020 Oct;53:212-220. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.08.006. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Breast. 2020. PMID: 32890963 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) Predict Clinical Outcome in Patients with Stage IIB Cervical Cancer.J Oncol. 2021 Sep 8;2021:2939162. doi: 10.1155/2021/2939162. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34539781 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of preoperative lymphocyte-related systemic inflammatory biomarkers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Oct 23;18(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-02048-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33097052 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, or Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Endometrial Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 May 16;12:734948. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.734948. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35651788 Free PMC article.
-
Can Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio at Day +100 be used as a prognostic marker in Multiple Myeloma patients with autologous transplantation?Clin Transplant. 2018 Sep;32(9):e13359. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13359. Epub 2018 Aug 26. Clin Transplant. 2018. PMID: 30053318
Cited by
-
Association of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Absolute Lymphocyte Count With Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Breast Cancer in the MONARCH 2 Trial.Oncologist. 2024 Mar 4;29(3):e319-e329. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad301. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 37971418 Free PMC article.
-
Ratios of monocytes and neutrophils to lymphocytes in the blood predict benefit of CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment in metastatic breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 2;13(1):21262. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47874-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38040730 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of systemic immune-inflammatory markers before and after treatment for pathological complete response in patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy for breast cancer: a retrospective study of 1994 patients.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Jun;26(6):1467-1479. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03371-7. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38190034
-
High C-reactive protein is associated with the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 29;103(48):e40775. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040775. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39612416 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Targeting Nanoliposome Improves Proinflammatory Immunomodulation of the Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Dec;12(31):e2302046. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302046. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 37605325 Free PMC article.

