Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the duodenal papilla with hepatic metastases: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 36003790
- PMCID: PMC9393733
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.948892
Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the duodenal papilla with hepatic metastases: A case report and literature review
Abstract
Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the duodenum is a rare special type of adenocarcinoma, featured by hepatocyte components in primary adenocarcinoma of the duodenum. It has the characteristics of high malignancy, invasiveness, rapid progress, and poor prognosis. An abnormal elevation of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) may occur in most cases. The diagnosis is mainly based on pathological morphology. Here, we reported a case of hepatic adenocarcinoma of the duodenum. The middle-aged female patient had an ampulla mass at diagnosis and received radical pancreaticoduodenectomy. The postoperative pathology was stage IIIA duodenal adenocarcinoma. At 1 month after surgery, she had multiple intrahepatic metastases and retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis; the AFP level was 300 ng/ml at that time. As she refused target therapy, two cycles of capecitabine-oxaliplatin (XELOX) chemotherapy were performed. However, the AFP elevated from 300 to 1,931.90 ng/ml, and the disease progressed rapidly. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) of tissue samples from presurgical endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA), surgery, and liver biopsy showed positive AFP staining. Combining the abnormal elevation of serum AFP and microscopic pathological morphology, this case is diagnosed as hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the duodenum with liver metastasis. The physical condition of this patient was too poor to receive follow-up treatment. She died of the rapid disease progression with an overall survival time of 161 days. Considering that in most patients with hepatoid adenocarcinoma the abnormal elevation of serum AFP occurs preoperatively and returns to normal postoperatively rather than normal before surgery and increased after surgery, the primary lesion is located in the stomach rather than the intestine, and the patients are more often older men rather than middle-aged women; this case is rare particularly. Therefore, reporting this case with complete case data may be helpful to further study, so as to improve the understanding of this special type of malignant tumor.
Keywords: alpha- fetoprotein (AFP); hepatic metastases; hepatoid adenocarcinoma; hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the duodenum; immunohistochemical.
Copyright © 2022 Han, Ding, Li, Wei, Hu, Liu and Qian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
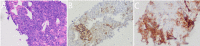
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis of gastric hepatoid adenocarcinoma].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Sep 25;20(9):1035-1039. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28900996 Chinese.
-
α-fetoprotein-producing gastric carcinoma: A case report of a rare subtype and literature review.Oncol Lett. 2016 May;11(5):3101-3104. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4372. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27123071 Free PMC article.
-
Emphasis on the clinical relationship between alpha-fetoprotein and hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach: a retrospective study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 May 9;23(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02773-9. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37161409 Free PMC article.
-
Non-α-fetoprotein-producing adrenal hepatoid adenocarcinoma: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Sep;97(39):e12336. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012336. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30278510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach.Gastric Cancer. 2001;4(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s101200100016. Gastric Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11706627 Review.
Cited by
-
An autopsy case of alpha-fetoprotein-producing large duodenal adenocarcinoma.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2023 Dec;16(6):829-835. doi: 10.1007/s12328-023-01843-5. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37594614
-
Risk factors, prognostic factors, and nomograms for distant metastasis in patients with diagnosed duodenal cancer: A population-based study.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Apr 15;16(4):1384-1420. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1384. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38660656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourreille J, Metayer P, Sauger F, Matray F, Fondimare A. Existence of alpha feto protein during gastric-origin secondary cancer of the liver. La Presse medicale (1970) 78:1277–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

