Volumetric modulated arc therapy versus tomotherapy for late T-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 36003797
- PMCID: PMC9393424
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.961781
Volumetric modulated arc therapy versus tomotherapy for late T-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the dosimetric parameters and clinical outcomes between volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) and tomotherapy for treating late T-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
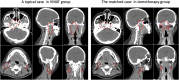
Methods: Patients with non-metastatic late T-stage NPC who received definitive radiotherapy with tomotherapy or VMAT were selected. 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) was used to control the balance of confounding factors. The dosimetric parameters and clinical outcomes were compared.
Results: A total of 171 patients were enrolled before matching, with 61 patients in the VMAT group and 110 patients in the tomotherapy group. In the post-PSM cohort, 54 sub-pairs of 108 patients were included after matching. Tomotherapy was superior to VMAT in the dosimetric parameters of planning target volumes, brainstem, spinal cord, lenses, and parotid glands but inferior in the optic nerves and optic chiasm. The tomotherapy group had a lower incidence of grade ≥ 3 acute mucositis (22.2% vs. 40.7%, p = 0.038) and a higher rate of complete response (83.3% vs. 66.7%, p = 0.046) after radiotherapy. However, there were no significant differences in locoregional failure-free survival (p = 0.375), distant metastasis-free survival (p = 0.529), or overall survival (p = 0.975) between the two groups.
Conclusion: Tomotherapy is superior to VMAT in terms of most dosimetric parameters, with less acute mucositis and better short-term efficacy. There are no significant differences in the survival outcomes between the VMAT and tomotherapy groups.
Keywords: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; VMAT; clinical outcomes; dosimetry; tomotherapy.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Tang, Zhu, Shen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dosimetric Comparisons of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy and Tomotherapy for Early T-Stage Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jun 4;2018:2653497. doi: 10.1155/2018/2653497. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29967769 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective matched study on comparison of volumetric-modulated arc therapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: dosimetry, delivery efficiency and outcomes.J Cancer. 2018 Feb 28;9(6):978-986. doi: 10.7150/jca.22843. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29581777 Free PMC article.
-
Volumetric modulated arc therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a dosimetric comparison with TomoTherapy and step-and-shoot IMRT.Radiother Oncol. 2012 Sep;104(3):324-30. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2011.11.017. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Radiother Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22236614
-
[Dosimetric comparison of the helical tomotherapy, intensity-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric-modulated arc therapy in radical radiotherapy for esophageal cancer].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Nov 5;99(41):3260-3265. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.41.012. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31694123 Chinese.
-
Comparison of Dosimetric Benefits of Three Precise Radiotherapy Techniques in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients Using a Priority-Classified Plan Optimization Model.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 27;11:646584. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.646584. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34646757 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma in adolescents treated with tomotherapy: Experience at King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre.Ann Saudi Med. 2024 May-Jun;44(3):153-160. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2024.153. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Ann Saudi Med. 2024. PMID: 38853474 Free PMC article.
-
Individualization of clinical target volume delineation in eccentric nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a prospective comparative study.Front Oncol. 2025 Aug 4;15:1587764. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1587764. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40831921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee FK, Yip CW, Cheung FC, Leung AK, Chau RM, Ngan RK. Dosimetric difference amongst 3 techniques: TomoTherapy, sliding-window intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), and RapidArc radiotherapy in the treatment of late-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Med Dosim (2014) 39(1):44–9. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2013.09.004 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

