Melatonin confers fenugreek tolerance to salinity stress by stimulating the biosynthesis processes of enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content
- PMID: 36003823
- PMCID: PMC9394454
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.890613
Melatonin confers fenugreek tolerance to salinity stress by stimulating the biosynthesis processes of enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content
Abstract
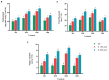
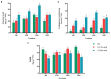
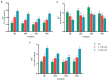
Salinity-induced stress is widely considered a main plant-growth-limiting factor. The positive effects of melatonin in modulating abiotic stresses have led this hormone to be referred to as a growth regulator in plants. This study aims to show how melatonin protects fenugreek against the negative effects of salt stress. Different amounts of melatonin (30, 60, and 90 ppm), salinity stress (150 mM and 300 mM), and the use of both salinity and melatonin were used as treatments. The results showed that applying different melatonin levels to salinity-treated fenugreek plants effectively prevented the degradation of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll, and carotenoid contents compared with salinity treatment without melatonin application. Besides, melatonin increases the biosynthesis of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants, thereby adjusting the content of reactive oxygen species, free radicals, electrolyte leakage, and malondialdehyde content. It was observed that applying melatonin increased the activity of potassium-carrying channels leading to the maintenance of ionic homeostasis and increased intracellular water content under salinity stress. The results revealed that melatonin activates the defense signaling pathways in fenugreek through the nitric oxide, auxin, and abscisic acid-dependent pathways. Melatonin, in a similar vein, increased the expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis pathway of diosgenin, a highly important steroidal sapogenin in medical and food industries, and hence the diosgenin content. When 150 mM salinity stress and 60 ppm melatonin were coupled, the diosgenin concentration rose by more than 5.5 times compared to the control condition. In conclusion, our findings demonstrate the potential of melatonin to enhance the plant tolerance to salinity stress by stimulating biochemical and physiological changes.
Keywords: fenugreek and diosgenin; melatonin; physiological changes; salinity stress.
Copyright © 2022 Mohamadi Esboei, Ebrahimi, Amerian and Alipour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exogenous 24-epibrassinolide ameliorates tolerance to high-temperature by adjusting the biosynthesis of pigments, enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content in fenugreek.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 24;13(1):6661. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33913-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37095206 Free PMC article.
-
Titanium dioxide -mediated regulation of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants, pigments, and diosgenin content promotes cold stress tolerance in Trigonella foenum-graecum L.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 13;15(1):1837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84472-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39805881 Free PMC article.
-
The amelioration of salt stress-induced damage in fenugreek through the application of cold plasma and melatonin.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Feb;207:108382. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108382. Epub 2024 Jan 21. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38271864
-
Recent advances and mechanistic insights on Melatonin-mediated salt stress signaling in plants.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022 Oct 1;188:97-107. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.08.007. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35995025 Review.
-
Role of Melatonin in Plant Tolerance to Soil Stressors: Salinity, pH and Heavy Metals.Molecules. 2020 Nov 17;25(22):5359. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225359. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33212772 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin Interaction with Other Phytohormones in the Regulation of Abiotic Stresses in Horticultural Plants.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 28;13(6):663. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060663. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic role of melatonin in enhancing temperature stress tolerance in fenugreek: coordination of antioxidant defense, hormonal regulation, energy status, sulfur metabolism, and diosgenin pathway genes.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Aug 26;25(1):1131. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-07224-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40859195
-
Melatonin Enhances Heat Tolerance via Increasing Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Osmotic Regulatory Substances by Upregulating zmeno1 Expression in Maize (Zea mays L.).Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 22;13(9):1144. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091144. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334803 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous 24-epibrassinolide ameliorates tolerance to high-temperature by adjusting the biosynthesis of pigments, enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content in fenugreek.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 24;13(1):6661. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33913-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37095206 Free PMC article.
-
Titanium dioxide -mediated regulation of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants, pigments, and diosgenin content promotes cold stress tolerance in Trigonella foenum-graecum L.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 13;15(1):1837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84472-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39805881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelova Z., Georgiev S., Roos W. (2006). Elicitation of plants. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 20, 72–83. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2006.10817345 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

