Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E family member nCBP facilitates the accumulation of TGB-encoding viruses by recognizing the viral coat protein in potato and tobacco
- PMID: 36003826
- PMCID: PMC9393630
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.946873
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E family member nCBP facilitates the accumulation of TGB-encoding viruses by recognizing the viral coat protein in potato and tobacco
Abstract
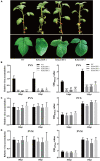
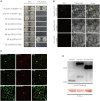
Due to their limited coding capacity, plant viruses have to depend on various host factors for successful infection of the host. Loss of function of these host factors will result in recessively inherited resistance, and therefore, these host factors are also described as susceptibility genes or recessive resistance genes. Most of the identified recessive resistance genes are members of the eukaryotic translation initiation factors 4E family (eIF4E) and its isoforms. Recently, an eIF4E-type gene, novel cap-binding protein (nCBP), was reported to be associated with the infection of several viruses encoding triple gene block proteins (TGBps) in Arabidopsis. Here, we, for the first time, report that the knockdown of nCBP in potato (StnCBP) compromises the accumulation of potato virus S (PVS) but not that of potato virus M (PVM) and potato virus X (PVX), which are three potato viruses encoding TGBps. Further assays demonstrated that StnCBP interacts with the coat proteins (CPs) of PVS and PVM but not with that of PVX, and substitution of PVS CP in the PVS infectious clone by PVM CP recovered the virus infection in StnCBP-silenced transgenic plants, suggesting that the recognition of PVS CP is crucial for StnCBP-mediated recessive resistance to PVS. Moreover, the knockdown of nCBP in Nicotiana benthamiana (NbnCBP) by virus-induced gene silencing suppressed PVX accumulation but not PVM, while NbnCBP interacted with the CPs of both PVX and PVM. Our results indicate that the nCBP orthologues in potato and tobacco have conserved function as in Arabidopsis in terms of recessive resistance against TGB-encoding viruses, and the interaction between nCBP and the CP of TGB-encoding virus is necessary but not sufficient to determine the function of nCBP as a susceptibility gene.
Keywords: TGB-encoding virus; coat protein; eukaryotic translation initiation factors 4E; nCBP; recessive resistance; susceptibility genes.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Yang, Tu, Xie, Chen, Luo, Hu, Nie and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deficiency of the eIF4E isoform nCBP limits the cell-to-cell movement of a plant virus encoding triple-gene-block proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 6;7:39678. doi: 10.1038/srep39678. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28059075 Free PMC article.
-
Complementation analysis of triple gene block of Potato virus S (PVS) revealed its capability to support systemic infection and aphid transmissibility of recombinant Potato virus X.Virus Res. 2009 Dec;146(1-2):81-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2009.09.003. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Virus Res. 2009. PMID: 19748533
-
Interaction of EXA1 and eIF4E Family Members Facilitates Potexvirus Infection in Arabidopsis thaliana.J Virol. 2023 Jun 29;97(6):e0022123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00221-23. Epub 2023 May 18. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37199623 Free PMC article.
-
[Recessive resistance to plant viruses by the deficiency of eukaryotic translation initiation factor genes.].Uirusu. 2020;70(1):61-68. doi: 10.2222/jsv.70.61. Uirusu. 2020. PMID: 33967115 Review. Japanese.
-
Molecular biology of resistance to potato virus X in potato.Biochem Soc Symp. 1994;60:207-18. Biochem Soc Symp. 1994. PMID: 7639780 Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing of potato StDMR6-1 results in plants less affected by different stress conditions.Hortic Res. 2024 May 6;11(7):uhae130. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae130. eCollection 2024 Jul. Hortic Res. 2024. PMID: 38974188 Free PMC article.
-
Plant eIF4E isoforms as factors of susceptibility and resistance to potyviruses.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 10;14:1041868. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1041868. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36844044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular characterization of a tetra segmented ssDNA virus infecting Botrytis cinerea worldwide.Virol J. 2023 Dec 19;20(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02256-z. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 38114992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brattey C., Badge J., Burns R., Foster G., George E., Goodfellow H., et al. (2002). Potato latent virus: a proposed new species in the genus Carlavirus. Plant Pathol. 51 495–505. 10.1046/j.1365-3059.2002.00729.x - DOI
-
- Cheng D., Zhou D., Wang Y., Wang B., He Q., Song B., et al. (2021). Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector RipV2 encoding a novel E3 ubiquitin ligase (NEL) is required for full virulence by suppressing plant PAMP-triggered immunity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 550 120–126. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.02.082 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

