An unusual case of Brown-Sequard syndrome associated with Horner's syndrome after a penetrating injury with a khuru (Bhutanese dart) to the neck: A case report
- PMID: 36003889
- PMCID: PMC9393493
- DOI: 10.1177/2050313X221116945
An unusual case of Brown-Sequard syndrome associated with Horner's syndrome after a penetrating injury with a khuru (Bhutanese dart) to the neck: A case report
Abstract
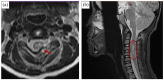
The occurrence of Brown-Sequard syndrome with Horner's syndrome in a child with spinal trauma is a very rare and unusual entity. Brown-Sequard syndrome results from hemisection injury of the spinal cord, mostly in the cervical cord region. The Horner's syndrome presents when the injury is in the cervical region involving the sympathetic pathway. We present you with the case of a 12-year-old boy who was referred from a local hospital with weakness on the left half of his body after sustaining a penetrating injury to his neck by a khuru (Bhutanese dart). Clinical examination was consistent with the diagnosis of Brown-Sequard syndrome with ipsilateral Horner's syndrome. Although cervical spine plain radiographs showed no fracture, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging showed a C2 lamina fracture at the left side of the spinous process with indentation to the cord. He was managed conservatively with a soft cervical collar, intravenous antibiotics, and physiotherapy. He had complete resolution of Brown-Sequard syndrome and Horner's syndrome after 1 year. Patients with Brown-Sequard syndrome associated with Horner's syndrome usually have a good prognosis and full recovery rate with regular physiotherapy and rehabilitation. Early diagnosis and treatment will have a better chance of recovery and return to pre-injury status.
Keywords: Brown-Sequard syndrome; Horner’s syndrome; cervical region; dart; khuru; penetrating injury.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Brown-Séquard syndrome without vascular injury associated with Horner's syndrome after a stab injury to the neck.J Spinal Cord Med. 2016;39(1):111-4. doi: 10.1179/2045772314Y.0000000297. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Spinal Cord Med. 2016. PMID: 25659820 Free PMC article.
-
Brown-Sequard syndrome associated with Horner's syndrome after a penetrating trauma at the cervicomedullary junction.Spinal Cord. 2000 Nov;38(11):705-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.sc.3101062. Spinal Cord. 2000. PMID: 11114780
-
Spontaneous cervical intradural disc herniation presenting with Brown-Séquard and Horner's syndrome: lesson learned from a very unique case.Eur Spine J. 2017 May;26(Suppl 1):218-221. doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-5044-4. Epub 2017 Mar 25. Eur Spine J. 2017. PMID: 28343313 Review.
-
Brown-Séquard syndrome associated with Horner's syndrome in cervical epidural hematoma.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995 Jan 15;20(2):244-7. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199501150-00023. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995. PMID: 7716632
-
Brown-Sèquard syndrome produced by C3-C4 cervical disc herniation: a case report and review of the literature.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008 Apr 20;33(9):E279-82. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31816c835d. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008. PMID: 18427307 Review.
References
-
- Rengachary SS, Colen C, Guthikonda M. Charles-Edouard Brown-Séquard: an eccentric genius. Neurosurgery 2008; 62(4): 954–964; discussion 964. - PubMed
-
- Shams S, Arain A. Brown Sequard syndrome. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing, 2022. - PubMed
-
- Van Wittenberghe IC, Peterson DC. Corticospinal tract lesion. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing, 2022. - PubMed
-
- García-Manzanares MD, Belda-Sanchis JI, Giner-Pascual M, et al.. Brown-Sequard syndrome associated with Horner’s syndrome after a penetrating trauma at the cervicomedullary junction. Spinal Cord 2000; 38(11): 705–707. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

