Serine ether glycerophospholipids: Decrements in the frontal cortex associated with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36004004
- PMCID: PMC9393623
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.981868
Serine ether glycerophospholipids: Decrements in the frontal cortex associated with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
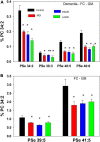
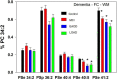
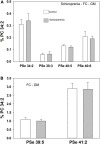
Ether glycerophospholipids (GPL) are involved in membrane fluidity and fusion. Vinyl-ether GPL are also conjectured to provide antioxidant capacity in the brain. The roles of these lipids in the processes involved in the development of dementia are not understood but choline and ethanolamine vinyl-ether GPL (i.e., plasmalogens) are decreased in the brains of subjects with dementia. In contrast, serine ether and vinyl-ether GPL have not been investigated in human brain. We therefore undertook an evaluation of these lipids, utilizing high-resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS), in tissues from control and dementia subjects that we had previously characterized in-depth. We can report for the first time that a number of serine ether GPL and a more limited number of serine plasmalogens are present in human frontal cortex. In addition, we found that some of these frontal cortex lipids are decreased in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), early-onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD), and late-onset AD (LOAD). In contrast no alterations in serine ether GPL were monitored in the frontal cortex of donors with schizophrenia, demonstrating disease specificity. These data suggest that further studies of the roles of ether GPL, including serine ether GPL, in brain function are worthy of undertaking.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; MCI; dementia; frontal cortex; serine ether glycerophospholipid.
Copyright © 2022 Wood and Woltjer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ether Lipid-Mediated Antioxidant Defense in Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;12(2):293. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020293. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-targeted lipidomics of CSF and frontal cortex grey and white matter in control, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's disease subjects.Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015 Oct;27(5):270-8. doi: 10.1017/neu.2015.18. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015. PMID: 25858158
-
Targeted lipidomics distinguishes patient subgroups in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and late onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD).BBA Clin. 2015 Nov 14;5:25-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2015.11.004. eCollection 2016 Jun. BBA Clin. 2015. PMID: 27051586 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of Ether-Type Glycerophospholipids, Plasmalogens, by NF-κB Signal Leading to Microglial Activation.J Neurosci. 2017 Apr 12;37(15):4074-4092. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3941-15.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 14. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28292831 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical methods for (oxidized) plasmalogens: Methodological aspects and applications.Free Radic Res. 2015 May;49(5):599-617. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.999675. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Free Radic Res. 2015. PMID: 25536419 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebral Gray and White Matter Monogalactosyl Diglyceride Levels Rise with the Progression of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;95(4):1623-1634. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230543. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37718815 Free PMC article.
-
Ether Lipid-Mediated Antioxidant Defense in Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;12(2):293. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020293. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brites P., Wanders R. J. A. (2004). Functions of plasmalogens in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1636 219–231. - PubMed
-
- Deeley J. M., Thomas M. C., Truscott R. J., Mitchell T. W., Blanksby S. J. (2009). Identification of abundant alkyl ether glycerophospholipids in the human lens by tandem mass spectrometry techniques. Anal. Chem. 81 1920–1930. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

