Laparoscopic versus Open Appendectomy: A Prospective Comparative Study and 4-Year Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital
- PMID: 36004006
- PMCID: PMC9395239
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1751112
Laparoscopic versus Open Appendectomy: A Prospective Comparative Study and 4-Year Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Abstract
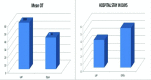
Background The aim of this study was to validate the pros of laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) over open appendectomy (OA) and to compare various primary outcome measures in the management of acute and recurrent appendicitis. Study Design Prospective comparative study. Place and Duration Between June 2015 and October 2019 in JJ Hospital, Mumbai. Materials and Methods Total of 60 patients with acute and recurrent appendicitis were included in the study. Thirty patients underwent OA and 30 underwent LA. Both groups were comparable clinicopathologically and demographically. Various intraoperative and postoperative parameters were compared. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and categorical variables were expressed as percentages. Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables and chi-squared test was used to compare categorical variables. p -Value≤0.001 was considered to be statistically significant. Results The median age of patients undergoing OA and LA was 24.9 and 25.2 years ( p = 0.221), respectively. Female: male ratio in OA and LA was 1.30 and 1.14, respectively ( p = 0.795). Mean operative duration in LA and OA group was 47.17 ± 14.39 minutes and 36.9 ± 12.33 minutes ( p = 0.001), respectively. Mean length of postoperative stay in LA and OA group was 3.69 ± 0.71 days and 5.28 ± 0.63 days ( p = 0.000), respectively. Median visual analogue scale score in LA and OA group was 3.5 and 5 ( p = 0.001), respectively. Mean time to return to normal activity in LA and OA group was 8.13 ± 1.33 days and 10.10 ± 2.20 days ( p = 0.000), respectively. About 6.66% patients in LA group and 13.33% in OA group had postoperative wound infection ( p = 0.652). Mean scar scale scoring done on 30th postoperative day was 4.23 in LA and 8.23 in OA ( p = 0.000). Discussion and Conclusion LA is more promising than OA in the management of acute and recurrent appendicitis. LA offers lesser operative site pain in the postoperative period, shorter postoperative hospital stays, earlier recovery, and return to normal activities and cosmetically better scars on 30th day follow-up. No conversions or significant difference in wound related complications were seen in both groups. Prolonged intraoperative duration was the only drawback of LA.
Keywords: acute; appendectomy; appendicitis; laparoscopic; recurrent.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Prospective and Comparative Study of Laparoscopic Appendectomy and Open Appendectomy in the Surgical Treatment of Appendicitis.Cureus. 2025 Jan 18;17(1):e77631. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77631. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39963643 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic vs open appendectomy. Prospective randomized study of outcomes.Arch Surg. 1997 Jul;132(7):708-11; discussion 712. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1997.01430310022003. Arch Surg. 1997. PMID: 9230853 Clinical Trial.
-
A prospective, randomized comparison of laparoscopic appendectomy with open appendectomy. Laparoscopic Appendectomy Study Group.Am J Surg. 1995 Feb;169(2):208-12; discussion 212-3. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(99)80138-x. Am J Surg. 1995. PMID: 7840381 Clinical Trial.
-
Open versus laparoscopic appendectomy in the pediatric population: a literature review and analysis of complications.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2012 Oct;22(8):834-9. doi: 10.1089/lap.2011.0492. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2012. PMID: 23039707 Review.
-
Laparoscopic versus conventional appendectomy--a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Gastroenterol. 2010 Nov 3;10:129. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-129. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21047410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Prospective and Comparative Study of Laparoscopic Appendectomy and Open Appendectomy in the Surgical Treatment of Appendicitis.Cureus. 2025 Jan 18;17(1):e77631. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77631. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39963643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Zhao Y Y, Qiao J, Ye R H. Diagnosis of appendicitis during pregnancy and perinatal outcome in the late pregnancy. Chin Med J (Engl) 2009;122(05):521–524. - PubMed
-
- Ozguner I F, Buyukayavuz B I, Savas M C. The influence of delay on perforation in childhood appendicitis. A retrospective analysis of 58 cases. Saudi Med J. 2004;25(09):1232–1236. - PubMed
-
- Semm K. Endoscopic appendectomy. Endoscopy. 1983;15(02):59–64. - PubMed
-
- Pier A, Götz F, Bacher C, Ibald R. Laparoscopic appendectomy. World J Surg. 1993;17(01):29–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

