A comprehensive review of methods based on deep learning for diabetes-related foot ulcers
- PMID: 36004341
- PMCID: PMC9394750
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.945020
A comprehensive review of methods based on deep learning for diabetes-related foot ulcers
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic disease with hyperglycemia. If not treated in time, it may lead to lower limb amputation. At the initial stage, the detection of diabetes-related foot ulcer (DFU) is very difficult. Deep learning has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in various fields and has been used to analyze images of DFUs.
Objective: This article reviewed current applications of deep learning to the early detection of DFU to avoid limb amputation or infection.
Methods: Relevant literature on deep learning models, including in the classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation for images of DFU, published during the past 10 years, were analyzed.
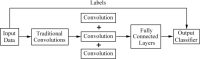
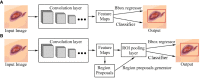
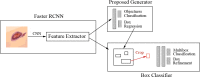
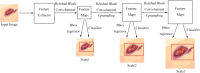
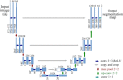
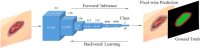
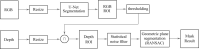
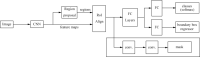
Results: Currently, the primary uses of deep learning in early DFU detection are related to different algorithms. For classification tasks, improved classification models were all based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The model with parallel convolutional layers based on GoogLeNet and the ensemble model outperformed the other models in classification accuracy. For object detection tasks, the models were based on architectures such as faster R-CNN, You-Only-Look-Once (YOLO) v3, YOLO v5, or EfficientDet. The refinements on YOLO v3 models achieved an accuracy of 91.95% and the model with an adaptive faster R-CNN architecture achieved a mean average precision (mAP) of 91.4%, which outperformed the other models. For semantic segmentation tasks, the models were based on architectures such as fully convolutional networks (FCNs), U-Net, V-Net, or SegNet. The model with U-Net outperformed the other models with an accuracy of 94.96%. Taking segmentation tasks as an example, the models were based on architectures such as mask R-CNN. The model with mask R-CNN obtained a precision value of 0.8632 and a mAP of 0.5084.
Conclusion: Although current research is promising in the ability of deep learning to improve a patient's quality of life, further research is required to better understand the mechanisms of deep learning for DFUs.
Keywords: classification; deep learning; diabetic foot ulcer; medical image; object detection; semantic segmentation.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Qiu, Peng, Zhou, Wang and Qi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deep learning in diabetic foot ulcers detection: A comprehensive evaluation.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Aug;135:104596. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104596. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34247133
-
Image segmentation using transfer learning and Fast R-CNN for diabetic foot wound treatments.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 20;10:969846. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.969846. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36203688 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of ischaemia and infection in diabetic foot ulcers: Dataset and techniques.Comput Biol Med. 2020 Feb;117:103616. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103616. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Comput Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32072964
-
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Identification: A Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 7;13(12):1998. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13121998. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Deep Learning in Computer Vision for Monitoring Apple Tree Growth and Fruit Production.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 12;25(8):2433. doi: 10.3390/s25082433. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40285123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A review of non-invasive sensors and artificial intelligence models for diabetic foot monitoring.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 21;13:924546. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.924546. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36338484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence Methodologies Applied to Technologies for Screening, Diagnosis and Care of the Diabetic Foot: A Narrative Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 8;12(11):985. doi: 10.3390/bios12110985. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Detection Model Using a Hybrid Convolutional Neural Networks-Vision Transformers.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 15;15(6):736. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060736. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150079 Free PMC article.
-
Smart diabetic foot ulcer scoring system.Sci Rep. 2024 May 21;14(1):11588. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62076-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38773207 Free PMC article.
-
A feature explainability-based deep learning technique for diabetic foot ulcer identification.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 25;15(1):6758. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90780-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40000748 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

