Applications of natural language processing in ophthalmology: present and future
- PMID: 36004369
- PMCID: PMC9393550
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.906554
Applications of natural language processing in ophthalmology: present and future
Abstract
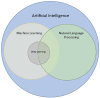
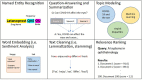
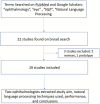
Advances in technology, including novel ophthalmic imaging devices and adoption of the electronic health record (EHR), have resulted in significantly increased data available for both clinical use and research in ophthalmology. While artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms have the potential to utilize these data to transform clinical care, current applications of AI in ophthalmology have focused mostly on image-based deep learning. Unstructured free-text in the EHR represents a tremendous amount of underutilized data in big data analyses and predictive AI. Natural language processing (NLP) is a type of AI involved in processing human language that can be used to develop automated algorithms using these vast quantities of available text data. The purpose of this review was to introduce ophthalmologists to NLP by (1) reviewing current applications of NLP in ophthalmology and (2) exploring potential applications of NLP. We reviewed current literature published in Pubmed and Google Scholar for articles related to NLP and ophthalmology, and used ancestor search to expand our references. Overall, we found 19 published studies of NLP in ophthalmology. The majority of these publications (16) focused on extracting specific text such as visual acuity from free-text notes for the purposes of quantitative analysis. Other applications included: domain embedding, predictive modeling, and topic modeling. Future ophthalmic applications of NLP may also focus on developing search engines for data within free-text notes, cleaning notes, automated question-answering, and translating ophthalmology notes for other specialties or for patients, especially with a growing interest in open notes. As medicine becomes more data-oriented, NLP offers increasing opportunities to augment our ability to harness free-text data and drive innovations in healthcare delivery and treatment of ophthalmic conditions.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; big data; data science; informatics; machine learning; natural language processing; ophthalmology.
Copyright © 2022 Chen and Baxter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

