Cationically modified inhalable nintedanib niosomes: enhancing therapeutic activity against non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 36004583
- PMCID: PMC9583758
- DOI: 10.2217/nnm-2022-0045
Cationically modified inhalable nintedanib niosomes: enhancing therapeutic activity against non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
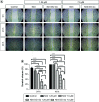
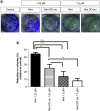
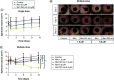
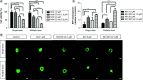
Aim: This study was designed to develop and test nintedanib-loaded niosomes as inhalable carriers for enhancing its therapeutic efficacy via localized drug accumulation and addressing issues such as low bioavailability and severe toxicity. Methods: Niosomes were prepared by thin-film hydration method and were evaluated for in vitro therapeutic effectiveness in lung cancer cells. Results: The optimized niosomal formulation displayed optimized vesicle size, controlled and extended release of drug, and efficient aerodynamic properties indicating its suitability as an aerosolized formulation. In vitro studies revealed significantly superior cytotoxicity of nintedanib-loaded niosomes which was further validated by 3D spheroids. Conclusion: These findings establish the effectiveness of niosomes as inhalable delivery carriers which could serve as a promising strategy for delivery of nintedanib to treat several lung cancers.
Keywords: aerosol; cationically modified vesicles; inhalable delivery carrier; nintedanib; niosomes; non-small-cell lung cancer; tyrosine kinase.
Figures
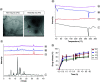
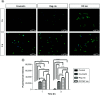
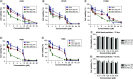
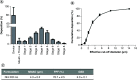
References
-
- American Cancer Society (2022). Lung cancer statistics: how common is lung cancer. www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
-
- WHO (2022). Cancer. www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
-
- National Cancer Institute. Browse the SEER cancer statistics review 1975–2017 (2020). https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/browse_csr.php?sectionSEL=15&pageS...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
