KRT5 missense variant in a Cardigan Welsh Corgi with epidermolysis bullosa simplex
- PMID: 36004757
- PMCID: PMC9804678
- DOI: 10.1111/age.13257
KRT5 missense variant in a Cardigan Welsh Corgi with epidermolysis bullosa simplex
Abstract
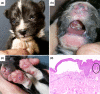
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of blistering disorders that includes several subtypes, classified according to their level of cleavage. Typical clinical signs are blisters and erosions resulting from minimal trauma. The disease has been described in many mammalian species and pathogenic variants in at least 18 different genes have been identified. In the present study, we investigated a Cardigan Welsh Corgi with congenital clinical signs consistent with epidermolysis bullosa. The puppy had blisters and erosions on the paw pads, and the oral mucosa. Histologic examination demonstrated the typical clefting between the dermis and epidermis and confirmed the clinical suspicion. We obtained whole genome sequencing data from the affected puppy and searched for variants in candidate genes known to cause EB. This revealed a heterozygous missense variant, KRT5:p.(E476K), affecting the highly conserved KLLEGE motif of keratin 5. The mutant allele in the affected puppy arose owing to a de novo mutation event as it was absent from both unaffected parents. Knowledge of the functional impact of KRT5 variants in other species together with the demonstration of the de novo mutation event establishes KRT5:p.(E476K) as causative variant for the observed EBS.
Keywords: Canis lupus familiaris; animal model; dermatology; dog; genodermatosis; precision medicine; skin; veterinary medicine.
© 2022 The Authors. Animal Genetics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Stichting International Foundation for Animal Genetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Capt, A. , Spirito, F. , Guaguere, E. , Spadafora, A. , Ortonne, J.‐P. & Meneguzzi, G. (2005) Inherited junctional epidermolysis bullosa in the German pointer: establishment of a large animal model. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 124(3), 530–535. 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.23584.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fine, J.‐D. , Eady, R.A.J. , Bauer, E.A. , Bauer, J.W. , Bruckner‐Tuderman, L. , Heagerty, A. et al. (2008) The classification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa (EB): report of the third international consensus meeting on diagnosis and classification of EB. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 58(6), 931–950. 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.02.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ford, C.A. , Stanfield, A.M. , Spelman, R.J. , Smits, B. , Ankersmidt‐Udy, A.E.L. , Cottier, K. et al. (2005) A mutation in bovine keratin 5 causing epidermolysis bullosa simplex, transmitted by a mosaic sire. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 124(6), 1170–1176. 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23610.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

