Mindfulness-based interventions for non-affective psychosis: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36004784
- PMCID: PMC9423825
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2108551
Mindfulness-based interventions for non-affective psychosis: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: Although mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) are routinely used in clinical practice, a comprehensive synthesis of the effectiveness of MBIs for non-affective psychosis has yet to be conducted. The aim of the present review and meta-analysis was to investigate the effectiveness of MBIs including those with mindfulness as an active treatment component for alleviating symptoms of psychosis to inform future clinical practice.
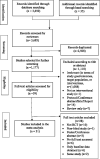
Methods: A systematic review of studies published in journals or in dissertations in CINAHL, PubMed, EMBASE, PsycINFO, CENTRAL, ISRCTN, or CNKI from January 1990 until December 2020. A total of 31 eligible studies (n = 2146) were included.
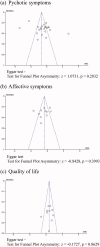
Results: Effect-size estimates suggested that 22 independent samples (n = 1632) produced a statistically significant small effect for psychotic symptoms (g = -0.48), and with a clinically significant reduction of 50% from baseline (pooled OR: 1.84). Separate meta-analyses demonstrated small effects for affective symptoms (g = -0.44) and small-to-large positive effects for quality of life (g = 0.38), mindfulness skills (g = 0.45), and insight into illness/treatment (g = 1.35). The heterogeneity was high across the studies.
Conclusion: Results suggest that short-term MBIs can be beneficial for non-affective psychosis. Future research is needed to test the efficacy and safety of dedicated MBIs for this population group over a longer term. KEY MESSAGESSchizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders, also known as non-affective psychosis, is the most chronic and debilitating type of psychosis, seriously affecting every aspect of a person's life, including social, occupational, or general functioning.The aim of the current systematic review and meta-analysis was to investigate formerly unexamined questions regarding the clinical significance of MBIs including yoga as an increasingly utilized, conceptualized psychological intervention on overall psychotic symptoms for people with non-affective psychosis.No serious adverse events were reported in the studies, suggesting that MBIs may be safe interventions, while there is robust evidence to support the view that MBIs are beneficial to young people in particular.
Keywords: Mindfulness-based interventions; effective to psychotic symptoms/affective symptoms/quality of life/mindfulness skills/insight into illness/treatment; longer-term duration; non-affective psychosis; younger people.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders-diagnostic criteria for research. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1993. p. 64–76.
-
- Keepers GA, Fochtmann LJ, Anzia JM, et al. . The American psychiatric association practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(9):868–872. - PubMed
-
- Lewis SW, Tarrier N, Drake RJ.. Integrating non-drug treatments in early schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2005;48:s65–s71. - PubMed
-
- Aust J, Bradshaw T.. Mindfulness interventions for psychosis: a systematic review of the literature. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2017;24(1):69–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
