Prognostic Role of Serum Adrenomedullin in Patients with Ventilator Associated Pneumonia
- PMID: 36004964
- PMCID: PMC9717343
- DOI: 10.3390/arm90040044
Prognostic Role of Serum Adrenomedullin in Patients with Ventilator Associated Pneumonia
Abstract
Objective: Ventilator associated pneumonia is a common type of sepsis that occurs to about 9-27% of all mechanically ventilated patients and 20-50% of them develop septic shock. Several clinical, laboratory, and radiological methods have been used for diagnosing VAP. Adrenomedullin (ADM) has been found to be elevated in the plasma of septic patients. The study aim was to explore the prognostic role of ADM in the VAP patients.
Design: A prospective observational study.
Setting: Intensive Care Department of Alexandria University Hospitals.
Patients: A total of 140 patients with proven VAP after medical ICU admission were consecutively enrolled.
Methods: APACHE II score, SOFA score, CRP, lactate, and serum ADM were measured at day 0 of VAP diagnosis and 5 days later. The results were correlated with the outcomes of patients.
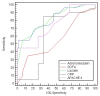
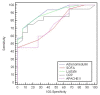
Results: APACHE II, lactate, and serum ADM on day 0 could predict an unfavorable outcome. ADM prediction power was significantly higher than APACHE II and lactate. Day 5 readings of all tested parameters could predict occurrence of the unfavorable outcome. ADM on day 0 showed the highest sensitivity (96.25%).
Conclusions: Serum adrenomedullin when measured at days 0 and 5 of VAP diagnosis may serve as an early predictor of unfavorable outcome.
Keywords: adrenomedullin; mortality; prolonged mechanical ventilation; sepsis; septic shock; ventilator associated pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating adrenomedullin estimates survival and reversibility of organ failure in sepsis: the prospective observational multinational Adrenomedullin and Outcome in Sepsis and Septic Shock-1 (AdrenOSS-1) study.Crit Care. 2018 Dec 21;22(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2243-2. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30583748 Free PMC article.
-
[The value of pro-adrenomedullin in early diagnosis of sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Sep;27(9):739-42. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26955700 Chinese.
-
[Application value of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis and severity assessment of ventilator-associated pneumonia].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Jun;33(6):702-707. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200824-00589. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 34296690 Chinese.
-
Adrenomedullin and Adrenomedullin-Targeted Therapy As Treatment Strategies Relevant for Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 19;9:292. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00292. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29520277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Adrenomedullin as a Predictive Marker of the Risk of Death and Adverse Clinical Events: A Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 16;13(16):4847. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164847. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200990 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Potential of Adrenomedullin Signaling in the Cardiovascular System.Circ Res. 2023 Apr 28;132(9):1185-1202. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.321673. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37104556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging Integrated RNA Sequencing to Decipher Adrenomedullin's Protective Mechanisms in Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jun 19;15(6):806. doi: 10.3390/genes15060806. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927741 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous