Optical Anisotropy and Excitons in MoS2 Interfaces for Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors
- PMID: 36004977
- PMCID: PMC9405904
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12080582
Optical Anisotropy and Excitons in MoS2 Interfaces for Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors
Abstract
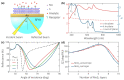
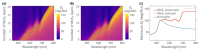
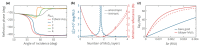
The use of ultra-thin spacer layers above metal has become a popular approach to the enhancement of optical sensitivity and immobilization efficiency of label-free SPR sensors. At the same time, the giant optical anisotropy inherent to transition metal dichalcogenides may significantly affect characteristics of the studied sensors. Here, we present a systematic study of the optical sensitivity of an SPR biosensor platform with auxiliary layers of MoS2. By performing the analysis in a broad spectral range, we reveal the effect of exciton-driven dielectric response of MoS2 and its anisotropy on the sensitivity characteristics. The excitons are responsible for the decrease in the optimal thickness of MoS2. Furthermore, despite the anisotropy being at record height, it affects the sensitivity only slightly, although the effect becomes stronger in the near-infrared spectral range, where it may lead to considerable change in the optimal design of the biosensor.
Keywords: MoS2; sensitivity enhancement; surface plasmon resonance; transition metal dichalcogenides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nylander C., Liedberg B., Lind T. Gas Detection by Means of Surface Plasmon Resonance. Sens. Actuators. 1982;3:79–88. doi: 10.1016/0250-6874(82)80008-5. - DOI
-
- Liedberg B., Nylander C., Lunström I. Surface Plasmon Resonance for Gas Detection and Biosensing. Sens. Actuators. 1983;4:299–304. doi: 10.1016/0250-6874(83)85036-7. - DOI
-
- Shalabney A., Abdulhalim I. Sensitivity-Enhancement Methods for Surface Plasmon Sensors. Laser Photon. Rev. 2011;5:571–606. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201000009. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

