1-L Transcription in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 36005139
- PMCID: PMC9406503
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb44080243
1-L Transcription in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
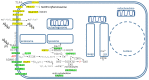
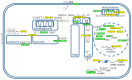
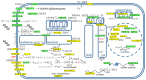
Alzheimer's disease is a very complex disease and better explanations and models are needed to understand how neurons are affected and microglia are activated. A new model of Alzheimer's disease is presented here, the β-amyloid peptide is considered an important RNA recognition/binding peptide. 1-L transcription revealed compatible sequences with AAUAAA (PAS signal) and UUUC (class III ARE rich in U) in the Aβ peptide, supporting the peptide-RNA regulatory model. When a hypothetical model of fibril selection with the prionic character of amyloid assemblies is added to the peptide-RNA regulatory model, the downregulation of the PI3K-Akt pathway and the upregulation of the PLC-IP3 pathway are well explained. The model explains why neurons are less protected from inflammation and why microglia are activated; why mitochondria are destabilized; why the autophagic flux is destabilized; and why the post-transcriptional attenuation of the axonal signal "noise" is interrupted. For example, the model suggests that Aβ peptide may post-transcriptionally control ELAVL2 (ELAV-like RNA binding protein 2) and DCP2 (decapping mRNA protein 2), which are known to regulate RNA processing, transport, and stability.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; bioinformatics method; identified genes; protein–RNA recognition code; β-amyloid peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Frisoni G.B., Altomare D., Thal D.R., Ribaldi F., van der Kant R., Ossenkoppele R., Blennow K., Cummings J., van Duijn C., Nilsson P.M., et al. The probabilistic model of alzheimer disease: The amyloid hypothesis revised. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022;23:53–66. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00533-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

