The Leucocyte Telomere Length, GSTM1 and GSTT1 Null Genotypes and the Risk of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 36005153
- PMCID: PMC9406937
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb44080257
The Leucocyte Telomere Length, GSTM1 and GSTT1 Null Genotypes and the Risk of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
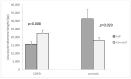
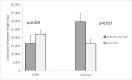
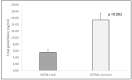
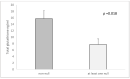
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by chronic inflammation and oxidative stress both in the airways and blood and other organs. Elevated oxidative stress and inflammation have been reported to affect leucocyte telomere length (LTL). Glutathione S-transferase (GST) enzymes are a large family of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes that utilize different ROS products. We aimed to explore the link between GSTM1 and GSTT1 gene polymorphisms, LTL and COPD risk. For GSTM1, we genotyped 152 COPD patients and 131 non-affected controls; for GSTT1, we genotyped 149 COPD patients and 130 controls. We were able to assess TL for 91 patients and 88 controls. There was a significant difference in the GSTM1 null genotype frequency between the patients and controls (0.59 vs. 0.38, p ≤ 0.000), but such was not found for GSTT1 (p = 0.192). When combining both polymorphisms, we obtained a significantly greater presence of at least one null genotype among patients (0.12 vs. 0.05, p = 0.027). An association between GSTT1 and LTL was not found. COPD patients carrying the GSTM1 null genotype had shorter telomeres compared to those carrying the non-null genotype (15,720 bp vs. 22,442 bp, p = 0.008); as for the controls, it was the opposite (31,354 bp vs. 17,800 bp, p = 0.020). The significance in both groups remained when combining GSTM1 and GSTT1 (COPD (at least one null) 16,409 bp vs. COPD (non-null) 22,092 bp, p = 0.029; control (at least one null) 29,666 bp vs. control (non-null) 16,370 bp, p = 0.027). The total glutathione level in GSTM1 non-null controls was higher compared to the null genotype (15.39 ng/mL vs. 5.53 ng/mL, p = 0.002). In COPD patients, we found no association (p = 0.301). In conclusion, according to our results, GSTM1, but not GSTT1, null genotypes might play a role in leucocyte telomere shortening, and thus be involved in the pathogenesis of COPD.
Keywords: COPD; GST; polymorphisms; telomeres.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic polymorphism of GSTT1 and GSTM1 and susceptibility to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).J Crit Care. 2009 Sep;24(3):e7-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2009.06.004. J Crit Care. 2009. PMID: 19664521
-
[Genetic polymorphisms of NQO1, GSTT1, GSTM1 and susceptibility to chronic benzene poisoning].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2005 Feb;23(1):1-5. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15748501 Chinese.
-
Combined analysis of EPHX1, GSTP1, GSTM1 and GSTT1 gene polymorphisms in relation to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease risk and lung function impairment.Dis Markers. 2011;30(5):253-63. doi: 10.3233/DMA-2011-0782. Dis Markers. 2011. PMID: 21734345 Free PMC article.
-
Association of GSTT1 and GSTM1 polymorphisms with early pregnancy loss in an Indian population and a meta-analysis.Reprod Biomed Online. 2013 Apr;26(4):313-22. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2012.12.004. Epub 2012 Dec 22. Reprod Biomed Online. 2013. PMID: 23433732 Review.
-
Association of glutathione S-transferase polymorphisms (GSTM1 and GSTT1) with primary open-angle glaucoma: an evidence-based meta-analysis.Gene. 2013 Sep 10;526(2):80-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.032. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23747403 Review.
Cited by
-
The micro-743a-3p-GSTM1 pathway is an endogenous protective mechanism against alcohol-related liver disease in mice.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Mar 12;29(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00557-x. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38475733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- From the Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2017. [(accessed on 11 July 2022)]. Available online: https://goldcopd.org.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

