Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs: New Insights into the Biology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 36005165
- PMCID: PMC9406833
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol29080427
Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs: New Insights into the Biology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
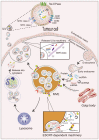
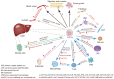
Exosomes, extracellular vesicles with a diameter of 40 to 160 nm, are among the smallest extracellular vesicles released by cells. They deliver different cargoes, including proteins, DNAs, and RNAs, and facilitate communication between cells to coordinate a variety of physiological and pathological functions. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth common malignant tumor and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Its molecular mechanism remains largely unknown, and there is a lack of reliable and noninvasive biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis prediction. Mounting evidence has shown that exosomes carry a variety of ncRNAs, such as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), which play critical roles in the occurrence and progression of HCC. In this review, we summarize the recent findings of exosomal miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in HCC from their impact on the development of HCC to their potential applications in the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
Keywords: exosome; hepatocellular carcinoma; long non-coding RNA; microRNA; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-coding RNAs in hepatitis C-induced hepatocellular carcinoma: dysregulation and implications for early detection, diagnosis and therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Nov 28;19(44):7836-45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.7836. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24307777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological functions and clinical applications of exosomal non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Nov;76(21):4203-4219. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03215-0. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31300868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Roles of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 24;12:790916. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.790916. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35280805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of exosomal noncoding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Carcinogenesis. 2022 Sep 19;43(8):754-765. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgac066. Carcinogenesis. 2022. PMID: 35904534
-
Non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Insights into regulatory mechanisms, clinical significance, and therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 10;13:985815. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.985815. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36300115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nomograms incorporating hsa_circ_0029325 highly expressed in exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma predict the postoperative outcomes.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jun 5;15(1):212. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01060-7. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38836972 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Delivery Vehicles for Non-Coding RNAs: Potential Biomarkers for Chronic Liver Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 26;14(3):277. doi: 10.3390/biom14030277. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of CTCF loop anchor based on machine learning.Front Genet. 2023 Apr 3;14:1181956. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1181956. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37077544 Free PMC article.
-
Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication of non-myeloid circulating cells in late sepsis based on single-cell RNA-seq.IET Syst Biol. 2024 Dec;18(6):218-226. doi: 10.1049/syb2.12109. Epub 2024 Nov 22. IET Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 39578684 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid gMLP model for interaction prediction of MHC-peptide and TCR.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 4;13:1092822. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1092822. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36685858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lötvall J., Hill A.F., Hochberg F., Buzás E.I., Di Vizio D., Gardiner C., Gho Y.S., Kurochkin I.V., Mathivanan S., Quesenberry P., et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2014;3:26913. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.26913. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu W., Liu C., Bi Z.Y., Zhou Q., Zhang H., Li L.L., Zhang J., Zhu W., Song Y.Y., Zhang F., et al. Comprehensive landscape of extracellular vesicle-derived RNAs in cancer initiation, progression, metastasis and cancer immunology. Mol. Cancer. 2020;19:102. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01199-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

