Donor-Site Morbidity and Quality of Life after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with PAP versus TMG Flap
- PMID: 36005186
- PMCID: PMC9406532
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol29080448
Donor-Site Morbidity and Quality of Life after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with PAP versus TMG Flap
Abstract
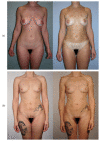
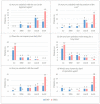
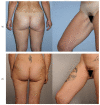
The transverse myocutaneous gracilis (TMG) and the profunda artery perforator (PAP) flap are both safe choices for autologous breast reconstruction originating from the same donor region in the upper thigh. We aimed to compare the post-operative outcome regarding donor-site morbidity and quality of life. We included 18 patients who had undergone autologous breast reconstruction with a PAP flap (n = 27 flaps). Prospective evaluation of donor-site morbidity was performed by applying the same questionnaire that had already been established in a previous study evaluating TMG flap (n = 25 flaps) outcome, and results were compared. Comparison of the two patient groups showed equivalent results concerning patient-reported visibility of the donor-site scar and thigh symmetry. Still, the TMG group was significantly more satisfied with the scar (p = 0.015) and its position (p = 0.001). No difference was found regarding the ability to sit for prolonged periods. Donor-site wound complications were seen more frequently in the PAP group (29.6%) than in the TMG group (4.0%). Both groups expressed rather high satisfaction with their quality of life. Both flaps show minimal functional donor-site morbidity and high patient satisfaction. To minimize wound healing problems in PAP patients, thorough planning of the skin paddle is necessary.
Keywords: PAP flap; TMG flap; autologous breast reconstruction; breast cancer; donor-site morbidity; mastectomy; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and donor site morbidity of the transverse musculocutaneous gracilis (TMG) flap in autologous breast reconstruction-A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Surg Oncol. 2021 Sep;124(4):492-509. doi: 10.1002/jso.26559. Epub 2021 Jun 6. J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34091906
-
Donor-site morbidity following harvest of the transverse myocutaneous gracilis flap for breast reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014 Nov;134(5):682e-691e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000612. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014. PMID: 25347642
-
Optimization of breast reconstruction results using TMG flap in 30 cases: Evaluation of several refinements addressing flap design, shaping techniques, and reduction of donor site morbidity.Microsurgery. 2018 Jul;38(5):489-497. doi: 10.1002/micr.30290. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Microsurgery. 2018. PMID: 29385241
-
The transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap for autologous breast reconstruction: focus on donor site morbidity.Breast Cancer. 2021 Nov;28(6):1273-1282. doi: 10.1007/s12282-021-01264-7. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Breast Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34091861 Free PMC article.
-
Lower Extremity Free Flaps for Breast Reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017 Nov;140(5S Advances in Breast Reconstruction):77S-86S. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003944. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017. PMID: 29064925 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the efficacy and safety of various flaps in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: a Bayesian network meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 20;11:1440139. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1440139. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39371345 Free PMC article.
-
A review of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering with a focus on wound healing and anti-aging.Front Surg. 2025 Jun 5;12:1504563. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1504563. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40538820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transverse myocutaneous gracilis flap (TMG) for breast reconstruction: ipsi vs. contralateral harvest-aesthetic outcome and refinement procedures.Breast Cancer. 2023 Sep;30(5):845-855. doi: 10.1007/s12282-023-01478-x. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37392247
-
Clinical Outcomes Following Profunda Artery Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Mar;49(5):1349-1368. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04441-z. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 39467864
-
Long-Term Results after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP versus PAP Flaps Based on Quality of Life and Aesthetic Outcome Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 17;12(3):737. doi: 10.3390/jcm12030737. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program SEER*Stat Database: Incidence-SEER Research Data. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2017–2019. [(accessed on 30 April 2022)]. Available online: http://www.Seer.Cancer.Gov.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

