Detection of Potential Mutated Genes Associated with Common Immunotherapy Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
- PMID: 36005189
- PMCID: PMC9406727
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol29080451
Detection of Potential Mutated Genes Associated with Common Immunotherapy Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
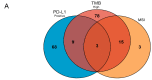
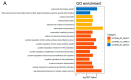
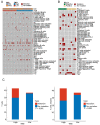
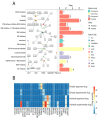
Microsatellite instability (MSI), high tumor mutation burden (TMB-H) and programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression are hot biomarkers related to the improvement of immunotherapy response. Two cohorts of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were collected and sequenced via targeted next-generation sequencing. Drug analysis was then performed on the shared genes using three different databases: Drugbank, DEPO and DRUGSURV. A total of 27 common genes were mutated in at least two groups of TMB-H-, MSI- and PD-L1-positive groups. AKT1, SMAD4, SCRIB and AXIN2 were severally involved in PI3K-activated, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)-activated, Hippo-repressed and Wnt-repressed pathways. This study provides an understanding of the mutated genes related to the immunotherapy biomarkers of NSCLC.
Keywords: gene mutation; immunotherapy; microsatellite instability; non-small-cell lung cancer; programmed cell death protein-1; tumor mutation burden.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

