Pharmacological Properties and Function of the PxOctβ3 Octopamine Receptor in Plutella xylostella (L.)
- PMID: 36005359
- PMCID: PMC9409995
- DOI: 10.3390/insects13080735
Pharmacological Properties and Function of the PxOctβ3 Octopamine Receptor in Plutella xylostella (L.)
Abstract
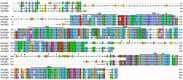
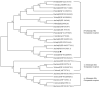
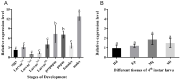
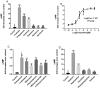
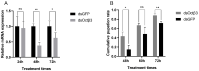
The diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella) is one of the most destructive lepidopteran pests of cruciferous vegetables, and insights into regulation of its physiological processes contribute towards the development of new pesticides against it. Thus, we investigated the regulatory functions of its β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor (PxOctβ3). The open reading frame (ORF) of PxOctβ3 was phylogenetically analyzed, and the levels of expression of the receptor mRNA were determined. This ORF was also cloned and expressed in HEK-293 cells. A series of octopamine receptor agonists and antagonists were tested against PxOctβ3. We showed that the receptor is a member of the Octβ3 protein family, and an analysis using quantitative PCR showed that it was expressed at all developmental stages of P. xylostella. Octopamine activated PxOctβ3, resulting in increased levels of intracellular cAMP. Furthermore, the agonists naphazoline, clonidine, 2-phenethylamine, and amitraz activated the PxOctβ3 receptor, and naphazoline was the most effective. Only metoclopramide and mianserin had significant antagonistic effects on PxOctβ3, whereas yohimbine, phentolamine, and chlorpromazine lacked obvious antagonistic effects. The injection of double-stranded RNA in an RNA interference assay indicated that PxOctβ3 regulates development in P. xylostella. This study demonstrated the pharmacological properties and functions of PxOctβ3 in P. xylostella, thus, providing a theoretical basis for the design of pesticides that target octopamine receptors.
Keywords: Plutella xylostella; RNAi; gene expression; octopamine receptor; pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological characterization of a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor in Plutella xylostella.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2018 Aug;98(4):e21466. doi: 10.1002/arch.21466. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29691888
-
Phenyl imidazolidin-2-ones antagonize a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor in diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella).Pest Manag Sci. 2021 Jul;77(7):3224-3232. doi: 10.1002/ps.6363. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Pest Manag Sci. 2021. PMID: 33723881
-
Pharmacological Properties of the Type 1 Tyramine Receptor in the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 17;20(12):2953. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122953. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212951 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Biogenic Amines in Oviposition by the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella L.Front Physiol. 2020 May 18;11:475. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00475. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32528307 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid selection for resistance to diamide insecticides in Plutella xylostella via specific amino acid polymorphisms in the ryanodine receptor.Neurotoxicology. 2017 May;60:224-233. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 May 28. Neurotoxicology. 2017. PMID: 27246647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and Pharmacological Characterization of β-Adrenergic-like Octopamine Receptors in the Endoparasitoid Cotesia chilonis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 22;23(23):14513. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314513. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498840 Free PMC article.
-
GABA and Octopamine Receptors as Potential Targets for Fumigant Actions of Bursera graveolens Essential Oil Against Callosobruchus maculatus and Callosobruchus chinensis.J Xenobiot. 2025 Jun 12;15(3):91. doi: 10.3390/jox15030091. J Xenobiot. 2025. PMID: 40558874 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

