Doxycycline Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Improving Myocardial Energy Metabolism in Rats
- PMID: 36005418
- PMCID: PMC9410319
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd9080254
Doxycycline Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Improving Myocardial Energy Metabolism in Rats
Abstract
Aim: Evaluate the influence of doxycycline, an anti-inflammatory and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor, on the attenuation of chronic doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.
Methods: We allocated male Wistar rats into four groups: control (C), doxorubicin (D), doxycycline (inhibitor of MMP, IM), and Dox + doxycycline (DIM). Groups IM and DIM received doxycycline (5 mg/kg, IP) once a week for 4 weeks. In addition, 48 h after every doxycycline injection, groups D and DIM received Dox (5 mg/kg, IP). We performed echocardiogram and evaluated TIMP-4 and collagen I protein expression, MMP-2 activity, and oxidative stress and myocardial metabolism.
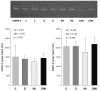
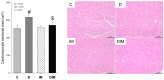
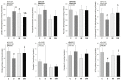
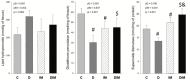
Results: Doxorubicin promotes left atrium (LA) and left ventricle (LV) dilatation and decreases in LV fractional shortening, which was improved by doxycycline. Moreover, doxycycline attenuated the LV cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and collagen type I expression. Doxorubicin increased phosphofructokinase and decreased beta-hydroxyacyl Co-A dehydrogenase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, and ATP synthase activity, which was partially attenuated by doxycycline. Lastly, doxycycline improved antioxidant enzyme activity in the DIM group.
Conclusion: Doxorubicin increases oxidative stress and promotes changes in myocardial energy metabolism, accompanied by structural and functional changes. Doxycycline attenuated the doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity, at least in part, through changes in myocardial energy metabolism.
Keywords: MMP-2; TIMP-4; collagen I; doxycycline; myocardial energy metabolism; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Euterpe oleracea Mart. (Açai) Supplementation Attenuates Acute Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rats.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;53(2):388-399. doi: 10.33594/000000145. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31403269
-
Pera orange (Citrus sinensis) and Moro orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) juices attenuate left ventricular dysfunction and oxidative stress and improve myocardial energy metabolism in acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.Nutrition. 2021 Nov-Dec;91-92:111350. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111350. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Nutrition. 2021. PMID: 34265580
-
Pamidronate Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Energetic Metabolism Changes but Worsens Functional Outcomes in Acute Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rats.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(3-4):431-442. doi: 10.1159/000452558. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27889760
-
[Effects of doxycycline on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of MMP in myocardium after acute myocardial infarction: an animal experiment with rats].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Aug 2;84(15):1288-93. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15387968 Chinese.
-
[Comparison of doxycycline, losartan, and their combination on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase, tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase, and collagen remodeling in the noninfarcted myocardium after acute myocardial infarction in rats].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2005 Feb;27(1):53-61. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 15782494 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Lady's Bedstraw as a Powerful Antioxidant for Attenuation of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 15;12(6):1277. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061277. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372007 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Mechanism, Monitoring, and Prevention of Cardiac Injury Caused by Antineoplastic Drugs-Anthracyclines.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 3;13(9):689. doi: 10.3390/biology13090689. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Gut-Heart Axis and Its Role in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Narrative Review.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 9;13(4):855. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040855. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitophagy in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Insights into Molecular Biology and Novel Therapeutic Strategies.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 17;14(12):1614. doi: 10.3390/biom14121614. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pera orange juice (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) alters lipid metabolism and attenuates oxidative stress in the heart and liver of rats treated with doxorubicin.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 23;10(17):e36834. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36834. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39263053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ribeiro A.P.D., Pereira A.G., Todo M.C., Fujimori A.S.S., dos Santos P.P., Dantas D., Fernandes A.A., Zanati S.G., Hassimotto N.M.A., Zornoff L.A.M., et al. Pera Orange (Citrus sinensis) and Moro Orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) Juices Attenuate Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress and Improve Myocardial Energy Metabolism in Acute Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rats. Nutrition. 2021;91–92:111350. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111350. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

