Serum vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with cardiovascular involvement and response to therapy in Erdheim-Chester disease
- PMID: 36005561
- PMCID: PMC9890031
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2022.280755
Serum vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with cardiovascular involvement and response to therapy in Erdheim-Chester disease
Abstract
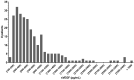
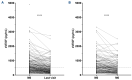
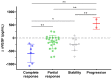
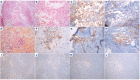
Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD) is a rare histiocytosis, considered to be an inflammatory myeloid neoplasm. Tropism for specific involvements of the disease remains unexplained. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF) is implicated in cancer pathophysiology and mutations of the RAS oncogene have been shown to induce upregulation of VEGF gene expression. We therefore hypothesized that VEGF might play a particular role in ECD pathophysiology. We conducted a retrospective, single-center study to assess serum VEGF (sVEGF) concentrations and determine whether they were associated with the characteristics of ECD patients, and to determine whether VEGF was expressed by histiocytes. We evaluated 247 ECD patients, 53.4% of whom had sVEGF levels above the normal range (>500 pg/mL). Patients with high sVEGF levels more frequently had cardiac and vascular involvement (58.3% vs. 41.4%, P=0.008 and 70.5% vs. 48.3%, P=0.0004, respectively). In treatment-naïve patients (n=135), the association of C-reactive protein >5 mg/L and sVEGF >500 pg/mL was strongly associated with vascular involvement (odds ratio=5.54 [95% confidence interval: 2.39-13.62], P<0.001), and independently associated with cardiac involvement (odds ratio=3.18 [95% confidence interval: 1.34-7.83], P=0.010) after adjustment for the presence of the BRAF V600E mutation. Changes in sVEGF concentration on treatment were associated with a response of cardiac involvement on consecutive cardiac magnetic resonance images. All histological samples analyzed (n=24) displayed histiocytes with intracytoplasmic expression of VEGF, which was moderate to high in more than 90% of cases. Our study suggests a role for VEGF in cardiac and vascular involvement in ECD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoalphalipoproteinemia and BRAFV600E Mutation Are Major Predictors of Aortic Infiltration in the Erdheim-Chester Disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Aug;38(8):1913-1925. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.310803. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29930009
-
The histiocytosis Erdheim-Chester disease is an inflammatory myeloid neoplasm.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015;11(9):1033-42. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2015.1060857. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26197238 Review.
-
Evaluation of clinicopathologic characteristics and the BRAF V600E mutation in Erdheim-Chester disease among Chinese adults.Ann Hematol. 2016 Apr;95(5):745-50. doi: 10.1007/s00277-016-2606-1. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Ann Hematol. 2016. PMID: 26858028
-
Abdominal involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD): MRI and CT imaging findings and their association with BRAFV600E mutation.Eur Radiol. 2018 Sep;28(9):3751-3759. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5326-1. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29556768
-
Erdheim-Chester Disease: a Concise Review.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019 Dec 5;21(12):66. doi: 10.1007/s11926-019-0865-2. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31807955 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic mechanism and key active ingredients of Yinxing Mihuan Oral Solution in coronary heart disease comorbidity with anxiety: A network pharmacology and molecular docking approach.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 25;103(43):e40183. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040183. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39470548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haroche J, Charlotte F, Arnaud L, et al. . High prevalence of BRAF V600E mutations in Erdheim-Chester disease but not in other non-Langerhans cell histiocytoses. Blood. 2012;120(13):2700-2703. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):669-676. - PubMed
-
- Rak J, Mitsuhashi Y, Bayko L, et al. . Mutant ras oncogenes upregulate VEGF/VPF expression: implications for induction and inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1995;55(20):4575-4580. - PubMed
-
- Dina A, Zahava V, Iness M. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2005;27(2):62-66. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

