Studies of Protein Wastes Adsorption by Chitosan-Modified Nanofibers Decorated with Dye Wastes in Batch and Continuous Flow Processes: Potential Environmental Applications
- PMID: 36005674
- PMCID: PMC9416031
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12080759
Studies of Protein Wastes Adsorption by Chitosan-Modified Nanofibers Decorated with Dye Wastes in Batch and Continuous Flow Processes: Potential Environmental Applications
Abstract
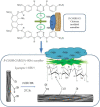
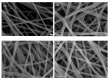
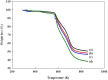
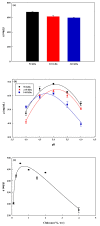
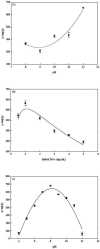
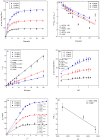
In this study, reactive green 19 dye from wastewater was immobilized on the functionalized chitosan nanofiber membranes to treat soluble microbial proteins in biological wastewater. Polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane (PAN) was prepared by the electrospinning technique. After heat treatment, alkaline hydrolysis, and chemically grafted with chitosan to obtain modified chitosan nanofibers (P-COOH-CS), and finally immobilized with RG19 dye, dyed nanofibers were generated (P-COOH-CS-RG19). The synthesis of P-COOH-CS and P-COOH-CS-RG19 are novel materials for protein adsorption that are not deeply investigated currently, with each of the material functions based on their properties in significantly improving the adsorption efficiency. The nanofiber membrane shows good adsorption capacity and great recycling performance, while the application of chitosan and dye acts as the crosslinker in the nanofiber membrane and consists of various functional groups to enhance the adsorption of protein. The dyed nanofibers were applied for the batch adsorption of soluble protein (i.e., lysozyme), and the process parameters including chitosan's molecular weight, coupling pH, chitosan concentration, dye pH, dye concentration, and lysozyme pH were studied. The results showed that the molecular weight of chitosan was 50 kDa, pH 5, concentration 0.5%, initial concentration of dye at 1 mg/mL dye and pH 12, lysozyme solution at 2 mg/mL at pH 8, and the maximum adsorption capacity was 1293.66 mg/g at a temperature of 318 K. Furthermore, thermodynamic, and kinetic studies suggested that the adsorption behavior of lysozyme followed the Langmuir adsorption isotherm model and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The optimal adsorption and desorption conditions based on batch experiments were directly applied to remove lysozyme in a continuous operation. This study demonstrated the potential of dyed nanofibers as an efficient adsorbent to remove approximately 100% of lysozyme from the simulated biological wastewater.
Keywords: chitosan; lysozyme; nanofiber membrane; reactive green 19 dye; removal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Meléndez-Ortiz H.I., Puente-Urbina B., Mercado-Silva J.A., García-Uriostegui L. Adsorption performance of mesoporous silicas towards a cationic dye. Influence of mesostructure on adsorption capacity. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2019;16:1533–1543. doi: 10.1111/ijac.13179. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

