Exosomes: Small Vesicles with Important Roles in the Development, Metastasis and Treatment of Breast Cancer
- PMID: 36005690
- PMCID: PMC9414313
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12080775
Exosomes: Small Vesicles with Important Roles in the Development, Metastasis and Treatment of Breast Cancer
Abstract
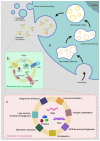
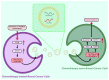
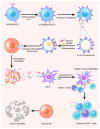
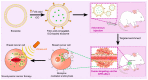
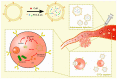
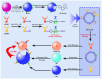
Breast cancer (BC) has now overtaken lung cancer as the most common cancer, while no biopredictive marker isolated from biological fluids has yet emerged clinically. After traditional chemotherapy, with the huge side effects brought by drugs, patients also suffer from the double affliction of drugs to the body while fighting cancer, and they often quickly develop drug resistance after the drug, leading to a poor prognosis. And the treatment of some breast cancer subtypes, such as triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), is even more difficult. Exosomes (Exos), which are naturally occurring extracellular vesicles (EVs) with nanoscale acellular structures ranging in diameter from 40 to 160 nm, can be isolated from various biological fluids and have been widely studied because they are derived from the cell membrane, have extremely small diameter, and are widely involved in various biological activities of the body. It can be used directly or modified to make derivatives or to make some analogs for the treatment of breast cancer. This review will focus on the involvement of exosomes in breast cancer initiation, progression, invasion as well as metastasis and the therapeutic role of exosomes in breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer therapeutics; drug resistance; exosome; targeted delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

