Interactions between the Nicotinic and Endocannabinoid Receptors at the Plasma Membrane
- PMID: 36005727
- PMCID: PMC9414690
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12080812
Interactions between the Nicotinic and Endocannabinoid Receptors at the Plasma Membrane
Abstract
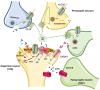
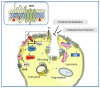
Compartmentalization, together with transbilayer and lateral asymmetries, provide the structural foundation for functional specializations at the cell surface, including the active role of the lipid microenvironment in the modulation of membrane-bound proteins. The chemical synapse, the site where neurotransmitter-coded signals are decoded by neurotransmitter receptors, adds another layer of complexity to the plasma membrane architectural intricacy, mainly due to the need to accommodate a sizeable number of molecules in a minute subcellular compartment with dimensions barely reaching the micrometer. In this review, we discuss how nature has developed suitable adjustments to accommodate different types of membrane-bound receptors and scaffolding proteins via membrane microdomains, and how this "effort-sharing" mechanism has evolved to optimize crosstalk, separation, or coupling, where/when appropriate. We focus on a fast ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptor, the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, and a second-messenger G-protein coupled receptor, the cannabinoid receptor, as a paradigmatic example.
Keywords: acetylcholine receptor; cannabinoid receptor; cannabinoids; membrane domains; nanodomains; neurotransmitter receptors; plasma membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanoscale Sub-Compartmentalization of the Dendritic Spine Compartment.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 15;11(11):1697. doi: 10.3390/biom11111697. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lipid habitats of neurotransmitter receptors in brain.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Nov;1858(11):2662-2670. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27424801 Review.
-
Alzheimer's Disease as a Membrane Disorder: Spatial Cross-Talk Among Beta-Amyloid Peptides, Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors and Lipid Rafts.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jul 18;13:309. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00309. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31379503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular approaches to the interaction between cannabinoid receptor ligands and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 May 15;731:100-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.03.010. Epub 2014 Mar 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24642359 Review.
-
Interactions between the endocannabinoid and nicotinic cholinergic systems: preclinical evidence and therapeutic perspectives.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 May;233(10):1765-77. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4196-3. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26728894 Review.
Cited by
-
A cholinergic circuit that relieves pain despite opioid tolerance.Neuron. 2023 Nov 1;111(21):3414-3434.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.08.017. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Neuron. 2023. PMID: 37734381 Free PMC article.
-
Adult consequences of repeated nicotine and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vapor inhalation in adolescent rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Mar;241(3):585-599. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06545-5. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38282127 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

