Cell cycle control by the insulin-like growth factor signal: at the crossroad between cell growth and mitotic regulation
- PMID: 36005738
- PMCID: PMC9769454
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2108117
Cell cycle control by the insulin-like growth factor signal: at the crossroad between cell growth and mitotic regulation
Abstract
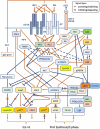
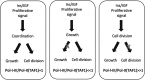
In proliferating cells and tissues a number of checkpoints (G1/S and G2/M) preceding cell division (M-phase) require the signal provided by growth factors present in serum. IGFs (I and II) have been demonstrated to constitute key intrinsic components of the peptidic active fraction of mammalian serum. In vivo genetic ablation studies have shown that the cellular signal triggered by the IGFs through their cellular receptors represents a non-replaceable requirement for cell growth and cell cycle progression. Retroactive and current evaluation of published literature sheds light on the intracellular circuitry activated by these factors providing us with a better picture of the pleiotropic mechanistic actions by which IGFs regulate both cell size and mitogenesis under developmental growth as well as in malignant proliferation. The present work aims to summarize the cumulative knowledge learned from the IGF ligands/receptors and their intracellular signaling transducers towards control of cell size and cell-cycle with particular focus to their actionable circuits in human cancer. Furthermore, we bring novel perspectives on key functional discriminants of the IGF growth-mitogenic pathway allowing re-evaluation on some of its signal components based upon established evidences.
Keywords: (scavenger protein for IGF2 & mannose-6-phosphate); GF; GH; HybR; HybR-A; IGF-I/II: insulin like growth factor peptides; IGF-Type I receptor gene; IGF1R; IGF1R/IR hybrid receptor; IGF1R/IR-A; IR (also InsR); IR isoform A (exon 11-); IR-A; IRS; Insulin-like growth factor receptor; RTK; growth factor; growth hormone; igf1/2; igf1r; igf2r/m6pr/SpI2-6; insr; insulin like growth factor genes; insulin receptor gene; insulin receptor protein; insulin receptor substrate; mTOR; mTOR complex. additional acronyms are clarified in the text; mTORC; mammalian target of rapamycin; property of a GF to increase growth (hypertrophy) and number (hyperplasia) of a target cell or tissue; receptor tyrosine kinase; trans-membrane high affinity IGF2 scavenger protein; trophic (effect); type I (protein).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Choi S, Sakamoto Y, et al. Purification of insulin receptor with full binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1983. Apr 25;258(8):5045–5049. - PubMed
-
- Ebina Y, Ellis L, Jarnagin K, et al. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985. Apr;40(4):747–758. - PubMed
-
- Ullrich A, Bell JR, Chen EY, et al. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. Nature. 1985. Feb-Mar 28-06;313(6005):756–761. - PubMed
-
- LeBon TR, Jacobs S, Cuatrecasas P, et al. Purification of insulin-like growth factor I receptor from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986. Jun 15;261(17):7685–7689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
